55 Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
OpenStax
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
- Derive chemical equations from narrative descriptions of chemical reactions.
- Write and balance chemical equations
An earlier chapter of this text introduced the use of element symbols to represent individual atoms. When atoms gain or lose electrons to yield ions, or combine with other atoms to form molecules, their symbols are modified or combined to generate chemical formulas that appropriately represent these species. Extending this symbolism to represent both the identities and the relative quantities of substances undergoing a chemical (or physical) change involves writing and balancing a chemical equation. Consider as an example the reaction between one methane molecule ([latex]\text{CH}_4[/latex]) and two diatomic oxygen molecules ([latex]\text{O}_2[/latex]) to produce one carbon dioxide molecule ([latex]\text{CO}_2[/latex]) and two water molecules ([latex]\text{H}_2\text{O}[/latex]). The chemical equation representing this process is provided in the upper half of the following figure, with space-filling molecular models shown in the lower half of the figure.
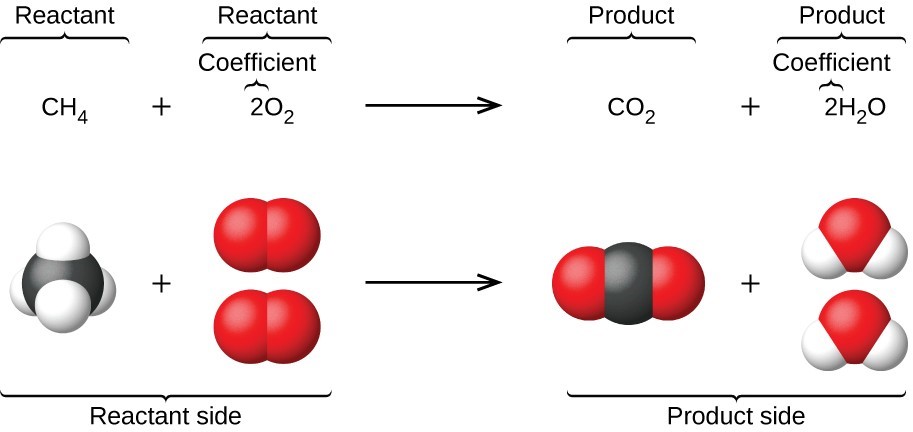
This example illustrates the fundamental aspects of any chemical equation:
- The substances undergoing reaction are called reactants, and their formulas are placed on the left side of the equation.
- The substances generated by the reaction are called products, and their formulas are placed on the right side of the equation.
- Plus signs (+) separate individual reactant and product formulas, and an arrow [latex]( \rightarrow )[/latex] separates the reactant and product (left and right) sides of the equation.
- The relative numbers of reactant and product species are represented by coefficients (numbers placed immediately to the left of each formula). A coefficient of 1 is typically omitted.
It is common practice to use the smallest possible whole-number coefficients in a chemical equation, as is done in this example. Realize, however, that these coefficients represent the relative numbers of reactants and products, and, therefore, they may be correctly interpreted as ratios. Methane and oxygen react to yield carbon dioxide and water in a 1:2:1:2 ratio. This ratio is satisfied if the numbers of these molecules are, respectively, 1-2-1-2, or 2-4-2-4, or 3-6-3-6, and so on. Likewise, these coefficients may be interpreted with regard to any amount (number) unit, and so this equation may be correctly read in many ways, including:
- One methane molecule and two oxygen molecules react to yield one carbon dioxide molecule and two water molecules.
- One dozen methane molecules and two dozen oxygen molecules react to yield one dozen carbon dioxide molecules and two dozen water molecules.
- One mole of methane molecules and 2 moles of oxygen molecules react to yield 1 mole of carbon dioxide molecules and 2 moles of water molecules. We will define the term "mole" later in the textbook.
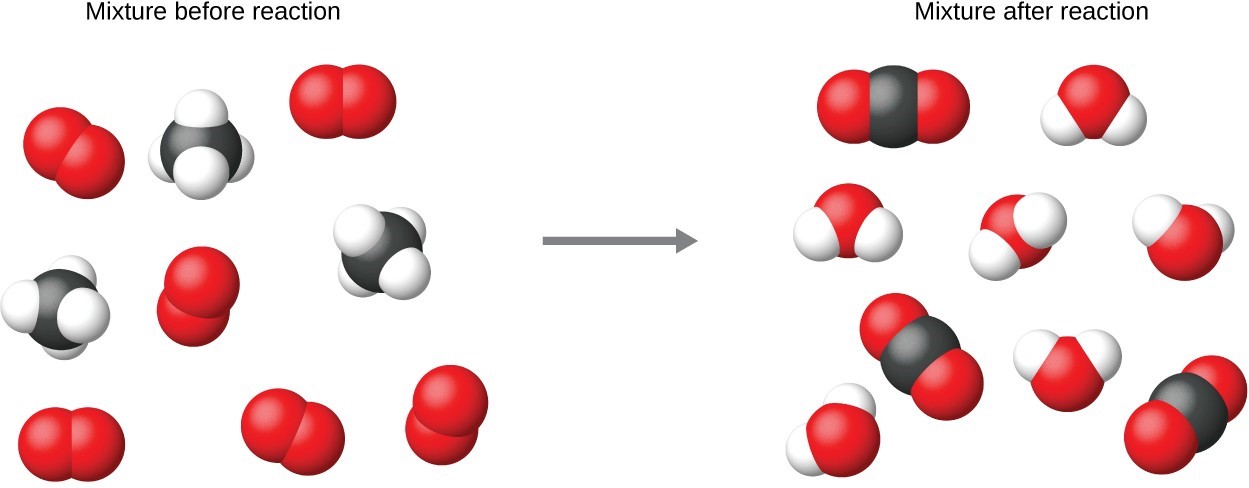
Figure 7.3: Regardless of the absolute numbers of molecules involved, the ratios between numbers of molecules of each species that react (the reactants) and molecules of each species that form (the products) are the same and are given by the chemical reaction equation.
Balancing Equations
The chemical equation described in section 4.1 is balanced, meaning that equal numbers of atoms for each element involved in the reaction are represented on the reactant and product sides. This is a requirement the equation must satisfy to be consistent with the law of conservation of matter. It may be confirmed by simply summing the numbers of atoms on either side of the arrow and comparing these sums to ensure they are equal. Note that the number of atoms for a given element is calculated by multiplying the coefficient of any formula containing that element by the element’s subscript in the formula. If an element appears in more than one formula on a given side of the equation, the number of atoms represented in each must be computed and then added together. For example, both product species in the example reaction, [latex]\text{CO}_2[/latex] and [latex]\text{H}_2\text{O}[/latex], contain the element oxygen, and so the number of oxygen atoms on the product side of the equation is
[latex]\left( \text{1 CO}_2 \text{ molecule} \times \frac{ \text{2 O atoms} }{ \text{CO}_2 \text{ molecule} } \right) + \left( \text{2 H}_2\text{O molecules} \times \frac{ \text{1 O atom} }{ \text{H}_2\text{O molecule} } \right) = \text{4 O atoms}[/latex]
The equation for the reaction between methane and oxygen to yield carbon dioxide and water is confirmed to be balanced per this approach, as shown here:
[latex]\text{CH}_4 + \text{2O}_2 \longrightarrow \text{CO}_2 + \text{2H}_2\text{O}[/latex]
| Element | Reactants | Products | Balanced? |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 1 × 1 = 1 | 1 × 1 = 1 | 1 = 1, yes |
| H | 4 × 1 = 4 | 2 × 2 = 4 | 4 = 4, yes |
| O | 2 × 2 = 4 | (1 × 2) + (2 × 1) = 4 | 4 = 4, yes |
A balanced chemical equation often may be derived from a qualitative description of some chemical reaction by a fairly simple approach known as balancing by inspection. Consider as an example the decomposition of water to yield molecular hydrogen and oxygen. This process is represented qualitatively by an unbalanced chemical equation:
[latex]\text{H}_2\text{O} \longrightarrow \text{H}_2 + \text{O}_2 \ \ \ \ \text{(unbalanced)}[/latex]
Comparing the number of H and O atoms on either side of this equation confirms its imbalance:
| Element | Reactants | Products | Balanced? |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | 1 × 2 = 2 | 1 × 2 = 2 | 2 = 2, yes |
| O | 1 × 1 = 1 | 1 × 2 = 2 | 1 ≠ 2, no |
The numbers of H atoms on the reactant and product sides of the equation are equal, but the numbers of O atoms are not. To achieve balance, the coefficients of the equation may be changed as needed. Keep in mind, of course, that the formula subscripts define, in part, the identity of the substance, and so these cannot be changed without altering the qualitative meaning of the equation. For example, changing the reactant formula from [latex]\text{H}_2\text{O}[/latex] to [latex]\text{H}_2\text{O}_2[/latex] would yield balance in the number of atoms, but doing so also changes the reactant’s identity (it’s now hydrogen peroxide and not water). The O atom balance may be achieved by changing the coefficient for [latex]\text{H}_2\text{O}[/latex] to 2.
[latex]\text{2H}_2\text{O} \longrightarrow \text{H}_2 + \text{O}_2 \ \ \ \ \text{(unbalanced)}[/latex]
| Element | Reactants | Products | Balanced? |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | 2 × 2 = 4 | 1 × 2 = 2 | 4 ≠ 2, no |
| O | 2 × 1 = 2 | 1 × 2 = 2 | 2 = 2, yes |
The H atom balance was upset by this change, but it is easily reestablished by changing the coefficient for the [latex]\text{H}_2[/latex] product to 2.
[latex]\text{2H}_2\text{O} \longrightarrow \text{2H}_2 + \text{O}_2 \ \ \ \ \text{(balanced)}[/latex]
| Element | Reactants | Products | Balanced? |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | 2 × 2 = 4 | 2 × 2 = 4 | 4 = 4, yes |
| O | 2 × 1 = 2 | 1 × 2 = 2 | 2 = 2, yes |
These coefficients yield equal numbers of both H and O atoms on the reactant and product sides, and the balanced equation is, therefore:
[latex]\text{2H}_2\text{O} \longrightarrow \text{2H}_2 + \text{O}_2[/latex]
EXAMPLE
Balancing Chemical Equations
Write a balanced equation for the reaction of molecular nitrogen ([latex]\text{N}_2[/latex]) and oxygen ([latex]\text{O}_2[/latex]) to form dinitrogen pentoxide.
Solution
First, write the unbalanced equation.
[latex]\text{N}_2 + \text{O}_2 \longrightarrow \text{N}_2\text{O}_5 \ \ \ \ \text{(unbalanced)}[/latex]
Next, count the number of each type of atom present in the unbalanced equation.
| Element | Reactants | Products | Balanced? |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 1 × 2 = 2 | 1 × 2 = 2 | 2 = 2, yes |
| O | 1 × 2 = 2 | 1 × 5 = 5 | 2 ≠ 5, no |
Though nitrogen is balanced, changes in coefficients are needed to balance the number of oxygen atoms. To balance the number of oxygen atoms, a reasonable first attempt would be to change the coefficients for the [latex]\text{O}_2[/latex] and [latex]\text{N}_2\text{O}_5[/latex] to integers that will yield 10 O atoms (the least common multiple for the O atom subscripts in these two formulas).
[latex]\text{N}_2 + \text{5O}_2 \longrightarrow \text{2N}_2\text{O}_5 \ \ \ \ \text{(unbalanced)}[/latex]
| Element | Reactants | Products | Balanced? |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 1 × 2 = 2 | 2 × 2 = 4 | 2 ≠ 4, no |
| O | 5 × 2 = 10 | 2 × 5 = 10 | 10 = 10, yes |
The N atom balance has been upset by this change; it is restored by changing the coefficient for the reactant [latex]\text{N}_2[/latex] to 2.
[latex]\text{2N}_2 + \text{5O}_2 \longrightarrow \text{2N}_2\text{O}_5[/latex]
| Element | Reactants | Products | Balanced? |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 2 × 2 = 4 | 2 × 2 = 4 | 4 = 4, yes |
| O | 5 × 2 = 10 | 2 × 5 = 10 | 10 = 10, yes |
The numbers of N and O atoms on either side of the equation are now equal, and so the equation is balanced.
Check Your Learning
Write a balanced equation for the decomposition of ammonium nitrate to form molecular nitrogen, molecular oxygen, and water. (Hint: Balance oxygen last, since it is present in more than one molecule on the right side of the equation.)
[latex]\text{2NH}_4\text{NO}_3 \longrightarrow \text{2N}_2 + \text{O}_2 + \text{4H}_2\text{O}[/latex]
It is sometimes convenient to use fractions instead of integers as intermediate coefficients in the process of balancing a chemical equation. When balance is achieved, all the equation’s coefficients may then be multiplied by a whole number to convert the fractional coefficients to integers without upsetting the atom balance. For example, consider the reaction of ethane ([latex]\text{C}_2\text{H}_6[/latex]) with oxygen to yield [latex]\text{H}_2\text{O}[/latex] and [latex]\text{CO}_2[/latex], represented by the unbalanced equation:
[latex]\text{C}_2\text{H}_6 + \text{O}_2 \longrightarrow \text{H}_2\text{O} + \text{CO}_2 \ \ \ \ \text{(unbalanced)}[/latex]
Following the usual inspection approach, one might first balance C and H atoms by changing the coefficients for the two product species, as shown:
[latex]\text{C}_2\text{H}_6 + \text{O}_2 \longrightarrow \text{3H}_2\text{O} + 2\text{CO}_2 \ \ \ \ \text{(unbalanced)}[/latex]
This results in seven O atoms on the product side of the equation, an odd number—no integer coefficient can be used with the [latex]\text{O}_2[/latex] reactant to yield an odd number, so a fractional coefficient, [latex]\frac{7}{2}[/latex], is used instead to yield a provisional balanced equation:
[latex]\text{C}_2\text{H}_6 + \frac{7}{2}\text{O}_2 \longrightarrow \text{3H}_2\text{O} + \text{2CO}_2[/latex]
A conventional balanced equation with integer-only coefficients is derived by multiplying each coefficient by 2:
[latex]\text{2C}_2\text{H}_6 + \text{7O}_2 \longrightarrow \text{6H}_2\text{O} + 4\text{CO}_2[/latex]
Finally with regard to balanced equations, recall that convention dictates use of the smallest whole-number coefficients. Although the equation for the reaction between molecular nitrogen and molecular hydrogen to produce ammonia is, indeed, balanced,
[latex]\text{3N}_2 + \text{9H}_2 \longrightarrow \text{6NH}_3[/latex]
the coefficients are not the smallest possible integers representing the relative numbers of reactant and product molecules. Dividing each coefficient by the greatest common factor, 3, gives the preferred equation:
[latex]\text{N}_2 + \text{3H}_2 \longrightarrow \text{2NH}_3[/latex]
Use this interactive tutorial for additional practice balancing equations.
Additional Information in Chemical Equations
The physical states of reactants and products in chemical equations very often are indicated with a parenthetical abbreviation following the formulas. Common abbreviations include s for solids, l for liquids, g for gases, and aq for substances dissolved in water (aqueous solutions, as introduced in the preceding chapter). These notations are illustrated in the example equation here:
[latex]\text{2Na} (s) + \text{2H}_2\text{O} (l) \longrightarrow \text{2NaOH} (aq) + \text{H}_2 (g)[/latex]
This equation represents the reaction that takes place when sodium metal is placed in water. The solid sodium reacts with liquid water to produce molecular hydrogen gas and the ionic compound sodium hydroxide (a solid in pure form, but readily dissolved in water).
Special conditions necessary for a reaction are sometimes designated by writing a word or symbol above or below the equation’s arrow. For example, a reaction carried out by heating may be indicated by the uppercase Greek letter delta (Δ) over the arrow.
[latex]\text{CaCO}_3 (s) \xrightarrow{\Delta} \text{CaO} (s) + \text{CO}_2 (g)[/latex]
Other examples of these special conditions will be encountered in more depth in later chapters.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Chemical equations are symbolic representations of chemical and physical changes. Formulas for the substances undergoing the change (reactants) and substances generated by the change (products) are separated by an arrow and preceded by integer coefficients indicating their relative numbers. Balanced equations are those whose coefficients result in equal numbers of atoms for each element in the reactants and products.
Chemistry End of Chapter Exercises
- What does it mean to say an equation is balanced? Why is it important for an equation to be balanced?
An equation is balanced when the same number of each element is represented on the reactant and product sides. Equations must be balanced to accurately reflect the law of conservation of matter.
- Balance the following equations:(a) [latex]\text{PCl}_5 (s) \text{ + H}_2\text{O} (l) \rightarrow \text{POCl}_3 (l) \text{ + HCl} (aq)[/latex](b) [latex]\text{Cu} (s) \text{ + HNO}_3 (aq) \rightarrow \text{Cu(NO}_3)_2 (aq) \text{ + H}_2\text{O} (l) \text{ + NO} (g)[/latex](c) [latex]\text{H}_2 (g) \text{ + I}_2 (s) \rightarrow \text{HI} (s)[/latex](d) [latex]\text{Fe} (s) \text{ + O}_2(g) \rightarrow \text{Fe}_2\text{O}_3 (s)[/latex](e) [latex]\text{Na} (s) \text{ + H}_2\text{O} (l) \rightarrow \text{NaOH} (aq) \text{ + H}_2 (g)[/latex](f) [latex]\text{(NH}_4)_2\text{Cr}_2\text{O}_7 (s) \rightarrow \text{Cr}_2\text{O}_3 (s) \text{ + N}_2 (g) \text{ + H}_2O (g)[/latex](g) [latex]\text{P}_4 (s) \text{ + Cl}_2 (g) \rightarrow \text{PCl}_3 (l)[/latex](h) [latex]\text{PtCl}_4 (s) \rightarrow \text{Pt} (s) \text{ + Cl}_2 (g)[/latex]
(a) [latex]\text{PCl}_5 (s) + \text{H}_2\text{O} (l) \rightarrow \text{POCl}_3 (l) \text{ + 2HCl} (aq)[/latex]; (b) [latex]\text{3Cu} (s) \text{ + 8HNO}_3 (aq) \rightarrow \text{3Cu(NO}_3)_2 (aq) \text{ + 4H}_2\text{O} (l) \text{ + 2NO} (g)[/latex];
(c) [latex]\text{H}_2 (g) \text{ + I}_2 (s) \rightarrow \text{2HI} (s)[/latex];
(d) [latex]\text{4Fe} (s) \text{ + 3O}_2 (g) \rightarrow \text{2Fe}_2\text{O}_3 (s)[/latex];
(e) [latex]\text{2Na} (s) + \text{2H}_2\text{O} (l) \rightarrow \text{2NaOH} (aq) \text{ + H}_2 (g)[/latex];
(f) [latex]\text{(NH}_4)_2\text{Cr}_2\text{O}_7 (s) \rightarrow \text{Cr}_2\text{O}_3 (s) \text{ + N}_2 (g) \text{ + 4H}_2\text{O} (g)[/latex];
(g) [latex]\text{P}_4 (s) \text{ + 6Cl}_2 (g) \rightarrow \text{4PCl}_3 (l)[/latex];
(h) [latex]\text{PtCl}_4 (s) \rightarrow \text{Pt} (s) \text{ + 2Cl}_2 (g)[/latex]
- Balance the following equations:
(a) [latex]\text{Ag} (s) \text{ + H}_2\text{S} (g) \text{ + O}_2 (g) \rightarrow \text{Ag}_2\text{S} (s) \text{ + H}_2\text{O} (l)[/latex](b) [latex]\text{P}_4 (s) \text{ + O}_2 (g) \rightarrow \text{P}_4\text{O}_{10} (s)[/latex](c) [latex]\text{Pb} (s) \text{+ H}_2\text{O} (l) \text{ + O}_2 (g) \rightarrow \text{Pb(OH)}_2 (s)[/latex](d) [latex]\text{Fe} (s) \text{ + H}_2\text{O} (l) \rightarrow \text{Fe}_3\text{O}_4 (s) \text{ + H}_2 (g)[/latex](e) [latex]\text{Sc}_2\text{O}_3 (s) \text{ + SO}_3 (l) \rightarrow \text{Sc}_2\text{(SO}_4)_3 (s)[/latex](f) [latex]\text{Ca}_3\text{(PO}_4)_2 (aq) \text{ + H}_3\text{PO}_4 (aq) \rightarrow \text{Ca(H}_2\text{PO}_4)_2 (aq)[/latex](g) [latex]\text{Al} (s) \text{ + H}_2\text{SO}_4 (aq) \rightarrow \text{Al}_2\text{(SO}_4)_3 (s) \text{ + H}_2 (g)[/latex](h) [latex]\text{TiCl}_4 (s) \text{ + H}_2\text{O} (g) \rightarrow \text{TiO}_2 (s) \text{ + HCl} (g)[/latex] - Write a balanced molecular equation describing each of the following chemical reactions. (a) Solid calcium carbonate is heated and decomposes to solid calcium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. (b) Gaseous butane, [latex]\text{C}_4\text{H}_{10}[/latex], reacts with diatomic oxygen gas to yield gaseous carbon dioxide and water vapor. (c) Aqueous solutions of magnesium chloride and sodium hydroxide react to produce solid magnesium hydroxide and aqueous sodium chloride. (d) Water vapor reacts with sodium metal to produce solid sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
(a) [latex]\text{CaCO}_3 (s) \rightarrow \text{CaO} (s) \text{ + CO}_2 (g)[/latex];(b) [latex]\text{2C}_4\text{H}_{10} (g) \text{ + 13O}_2 (g) \rightarrow \text{8CO}_2 (g) \text{ + 10H}_2\text{O} (g)[/latex];
(c) [latex]\text{MgCl}_2 (aq) \text{ + 2NaOH} (aq) \rightarrow \text{Mg(OH)}_2 (s) \text{ + 2NaCl} (aq)[/latex];
(d) [latex]\text{2H}_2\text{O} (g) \text{ + 2Na} (s) \rightarrow \text{2NaOH} (s) \text{ + H}_2 (g)[/latex]
- Write a balanced equation describing each of the following chemical reactions. (a) Solid potassium chlorate, [latex]\text{KClO}_3[/latex], decomposes to form solid potassium chloride and diatomic oxygen gas. (b) Solid aluminum metal reacts with solid diatomic iodine to form solid [latex]\text{Al}_2\text{I}_6[/latex]. (c) When solid sodium chloride is added to aqueous sulfuric acid, hydrogen chloride gas and aqueous sodium sulfate are produced. (d) Aqueous solutions of phosphoric acid and potassium hydroxide react to produce aqueous potassium dihydrogen phosphate and liquid water.
- Colorful fireworks often involve the decomposition of barium nitrate and potassium chlorate and the reaction of the metals magnesium, aluminum, and iron with oxygen. (a) Write the formulas of barium nitrate and potassium chlorate. (b) The decomposition of solid potassium chlorate leads to the formation of solid potassium chloride and diatomic oxygen gas. Write an equation for the reaction. (c) The decomposition of solid barium nitrate leads to the formation of solid barium oxide, diatomic nitrogen gas, and diatomic oxygen gas. Write an equation for the reaction. (d) Write separate equations for the reactions of the solid metals magnesium, aluminum, and iron with diatomic oxygen gas to yield the corresponding metal oxides. (Assume the iron oxide contains [latex]\text{Fe}^{3+}[/latex] ions.)
(a) [latex]\text{Ba(NO}_3)_2, \text{KClO}_3[/latex];(b) [latex]\text{2KClO}_3 (s) \rightarrow \text{2KCl} (s) \text{ + 3O}_2 (g)[/latex];
(c) [latex]\text{2Ba(NO}_3)_2 (s) \rightarrow \text{2BaO} (s) \text{ + 2N}_2 (g) \text{ + 5O}_2 (g)[/latex];
(d) [latex]\text{2Mg} (s) \text{ + O}_2 (g) \rightarrow \text{2MgO} (s)[/latex]; [latex]\text{4Al} (s) \text{ + 3O}_2 (g) \rightarrow \text{2Al}_2\text{O}_3 (s)[/latex]; [latex]\text{4Fe} (s) \text{ + 3O}_2 (g) \rightarrow \text{2Fe}_2\text{O}_3 (s)[/latex]
- Fill in the blank with a single chemical formula for a covalent compound that will balance the equation:
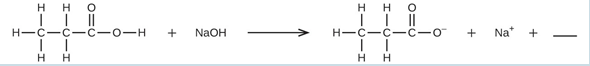
- Aqueous hydrogen fluoride (hydrofluoric acid) is used to etch glass and to analyze minerals for their silicon content. Hydrogen fluoride will also react with sand (silicon dioxide). (a) Write an equation for the reaction of solid silicon dioxide with hydrofluoric acid to yield gaseous silicon tetrafluoride and liquid water. (b) The mineral fluorite (calcium fluoride) occurs extensively in Illinois. Solid calcium fluoride can also be prepared by the reaction of aqueous solutions of calcium chloride and sodium fluoride, yielding aqueous sodium chloride as the other product. Write complete equations for this reaction[latex]\text{4HF} (aq) \text{ + SiO}_2(s) \rightarrow \text{SiF}_4(g) \text{ + 2H}_2\text{O}(l)[/latex];
- A novel process for obtaining magnesium from sea water involves several reactions. Write a balanced chemical equation for each step of the process. (a) The first step is the decomposition of solid calcium carbonate from seashells to form solid calcium oxide and gaseous carbon dioxide. (b) The second step is the formation of solid calcium hydroxide as the only product from the reaction of the solid calcium oxide with liquid water. (c) Solid calcium hydroxide is then added to the seawater, reacting with dissolved magnesium chloride to yield solid magnesium hydroxide and aqueous calcium chloride. (d) The solid magnesium hydroxide is added to a hydrochloric acid solution, producing dissolved magnesium chloride and liquid water. (e) Finally, the magnesium chloride is melted and electrolyzed to yield liquid magnesium metal and diatomic chlorine gas.
Glossary
- balanced equation
- chemical equation with equal numbers of atoms for each element in the reactant and product
- chemical equation
- symbolic representation of a chemical reaction
- coefficient
- number placed in front of symbols or formulas in a chemical equation to indicate their relative amount
- complete ionic equation
- chemical equation in which all dissolved ionic reactants and products, including spectator ions, are explicitly represented by formulas for their dissociated ions
- molecular equation
- chemical equation in which all reactants and products are represented as neutral substances
- net ionic equation
- chemical equation in which only those dissolved ionic reactants and products that undergo a chemical or physical change are represented (excludes spectator ions)
- product
- substance formed by a chemical or physical change; shown on the right side of the arrow in a chemical equation
- reactant
- substance undergoing a chemical or physical change; shown on the left side of the arrow in a chemical equation
- spectator ion
- ion that does not undergo a chemical or physical change during a reaction, but its presence is required to maintain charge neutrality
This chapter is an adaptation of the chapter “Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations” in Chemistry: Atoms First 2e by OpenStax and is licensed under a CC BY 4.0 license.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/chemistry-atoms-first-2e/pages/1-introduction
symbolic representation of a chemical reaction
substance undergoing a chemical or physical change; shown on the left side of the arrow in a chemical equation
substance formed by a chemical or physical change; shown on the right side of the arrow in a chemical equation
number placed in front of symbols or formulas in a chemical equation to indicate their relative amount
chemical equation with equal numbers of atoms for each element in the reactant and product
one of the three positions in a trigonal bipyramidal geometry with 120° angles between them; the axial positions are located at a 90° angle
property of a molecule that describes the separation of charge determined by the sum of the individual bond moments based on the molecular structure
separation of charge in a bond that depends on the difference in electronegativity and the bond distance represented by partial charges or a vector
(also, bond length) distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms
angle between any two covalent bonds that share a common atom
location in a trigonal bipyramidal geometry in which there is another atom at a 180° angle and the equatorial positions are at a 90° angle
force of attraction between nucleons that holds a nucleus together

