The Lateral Corticospinal Tract (Pyramidal Tract)
Caleb Bevan
Objective 8: Describe the lateral corticospinal tract.

Corticospinal Tract
The axons of Betz cells which leave primary motor cortex (Brodmann 4, precentral gyrus) and terminate on motor neurons in the spinal cord are collectively called the corticospinal tract. The first half of the word tells us where it came from and the second half tells us where it’s going; “tract” tells us it’s a bundle of axons in the central nervous system. An older name for this system is the pyramidal tract (so named because of the medullary pyramids they travel through, see below).
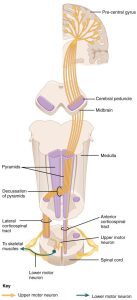 The pyramidal system is a single group of axons that, inexplicably, has seven names. Starting out as part of the
The pyramidal system is a single group of axons that, inexplicably, has seven names. Starting out as part of the
- corona radiata and part of the
- posterior limb of the internal capsule, it forms part of the
- crus cerebri which itself is part of the cerebral peduncles of the midbrain. In the pons, it reverts to the name
- corticospinal fibers before emerging on the ventral surface of the medulla as the
- pyramids, then crosses (decussates) at the
- decussation of the pyramids (at the level of the foramen magnum, the “big hole”in the bottom of the skull), then finally becomes the
- lateral corticospinal tract in the spinal cord.
Decussation is a word that derives from the same root as “decade” in English. Because the Roman numeral ten is represented by X, an X-like crossing is called a decussation (i.e., “making an X”)
The decussation of the pyramids is where the information from the left side of the brain crosses to the right side of the body, and vice versa.
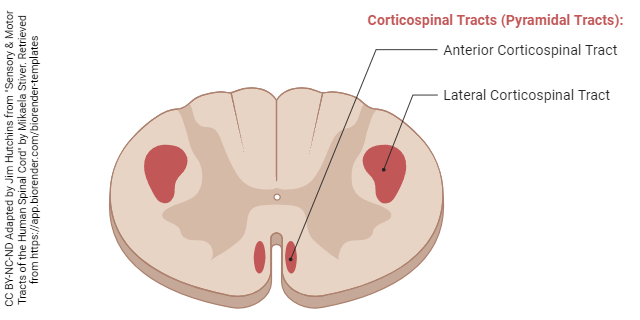
In the spinal cord, these fibers form two pathways. We’ll ignore the less important, uncrossed anterior corticospinal tract and focus on the lateral corticospinal tract. These axons, which started in the motor cortex of the brain, find the level they want (where the spinal nerve that controls the muscle is located), take a sharp right or left turn into the ventral (anterior) horn, and then make a synaptic contact onto the α motor neuron.
Media Attributions
- Giza Pyramids © Morhaf Kamal Aljanee is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Corticospinal tract © Betts, J. Gordon; Young, Kelly A.; Wise, James A.; Johnson, Eddie; Poe, Brandon; Kruse, Dean H. Korol, Oksana; Johnson, Jody E.; Womble, Mark & DeSaix, Peter is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Decussate © Jim Hutchins is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Motor Tracts of the Human Spinal Cord © Mikaela Stiver adapted by Jim Hutchins is licensed under a CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution NonCommercial NoDerivatives) license

