Optic Radiations
Jim Hutchins
Objective 11: Recognize key features of the pathway between the lateral geniculate nucleus and visual cortex (the optic radiations).
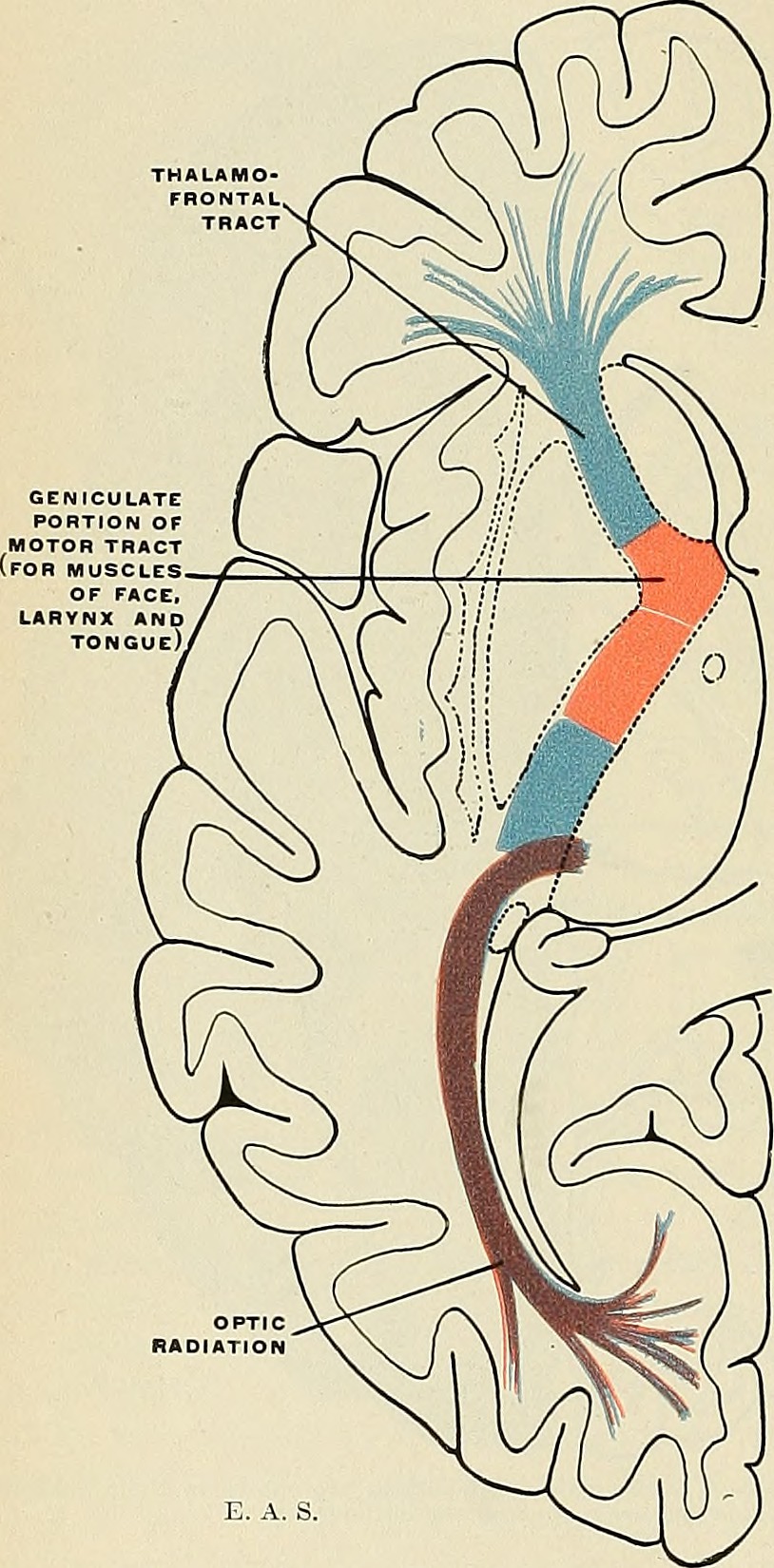
The cells of the M and P layers, along with the K cells, all send axons to primary visual cortex through tracts called the optic radiations. There is a split of LGN axons which received input from the superior retina on each side (representing the lower, inferior part of the visual field) and the LGN axons which received input from the inferior retina on each side (representing the upper, superior part of the visual field).
The axons which carry information from the inferior visual field are in the superior optic radiations and take a direct route to the occipital lobe.
The axons which carry information from the superior visual field are in the inferior optic radiations. These must circumvent the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle, forming a curved structure called Meyer’s Loop. Because the representation of the superior visual field takes a longer route, it is slightly more prone to damage.
When the fibers of Meyer’s Loop are damaged, a visual field defect called “pie in the sky” results. Axons representing a pie-shaped slice of the upper visual field on the contralateral side are damaged; because only ¼ of the visual field is affected on each side (contralateral & superior), this is called a homonymous quadrantanopsia (“same name [location] quarter [of the visual field] not seeing”).
Retinotopic Localization of Optic Radiation Fibers Projecting to Visual Cortex
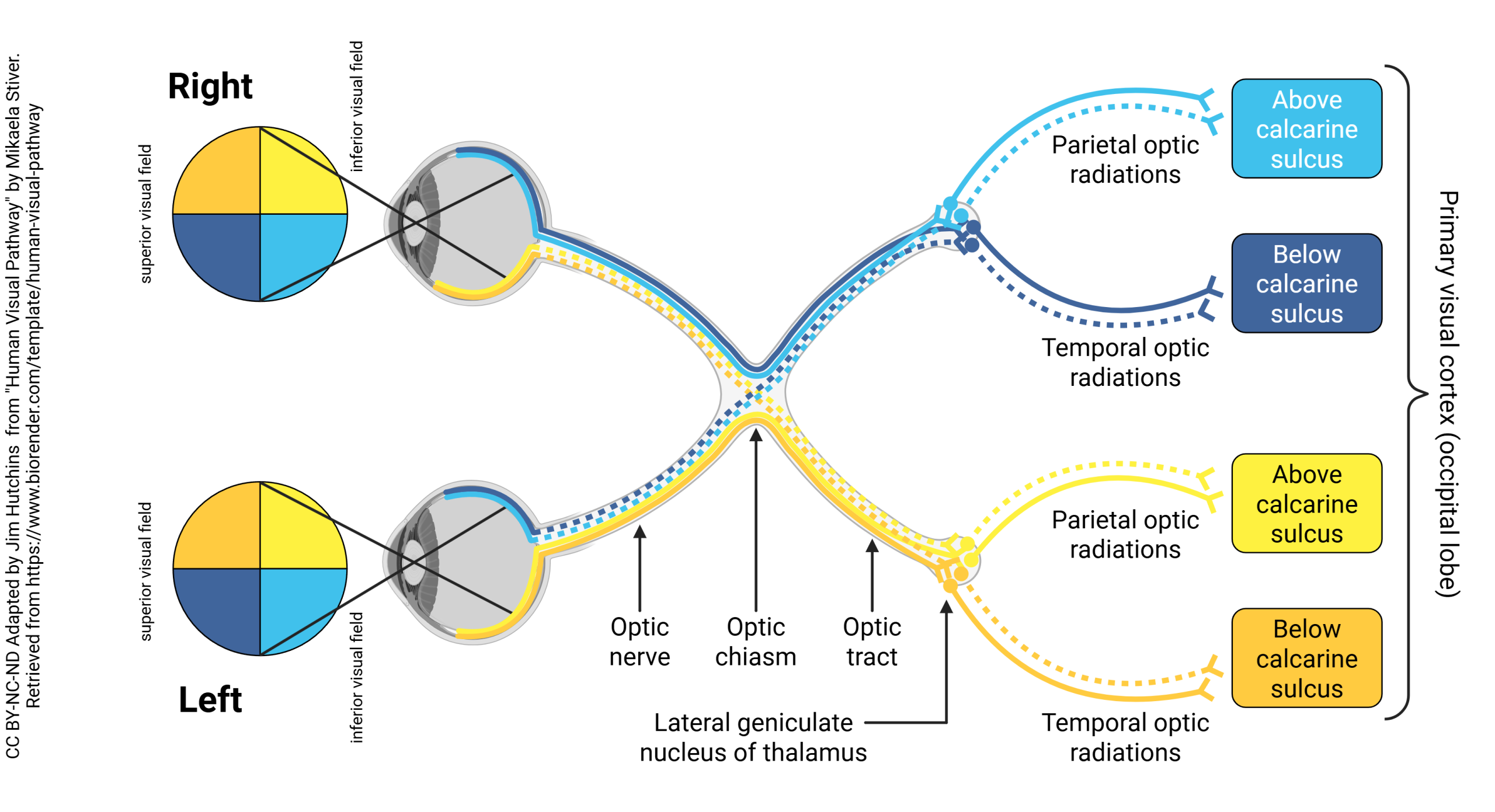
The pattern of axons in the visual pathway is represented in this diagram. The upper visual field is represented in royal blue (left) and orange (right), and the upper visual field in light blue (left) and yellow (right). For example, visual stimuli which appear in the upper right side of the visual field are represented by orange fibers. This information ends up being represented by visual cortical cells on the lower bank of the calcarine sulcus on the left side of the brain.
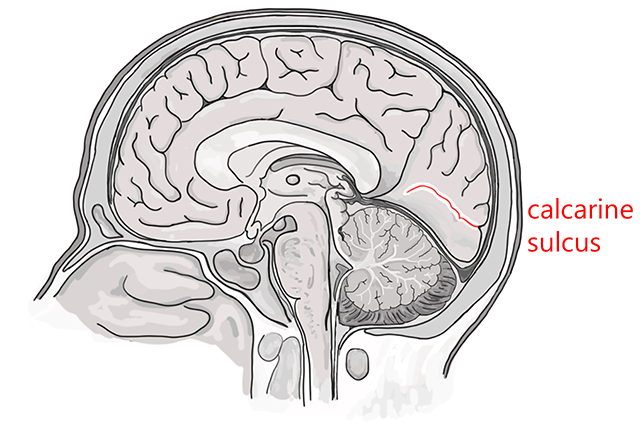
The calcarine sulcus is the physical, tangible representation of the imaginary line between the lower visual field representation and the upper visual field representation.
The lower visual field representation is on the upper (superior, dorsal) bank of the calcarine sulcus, in an area of the occipital cortex formally called the cuneus (Latin for “wedge”).
The upper visual field representation is on the lower (inferior, ventral) bank of the calcarine sulcus, in an area of the occipital cortex formally called the lingual gyrus. Lingual is from the Latin word for “tongue”, and of course a gyrus is a bump on the surface of the brain.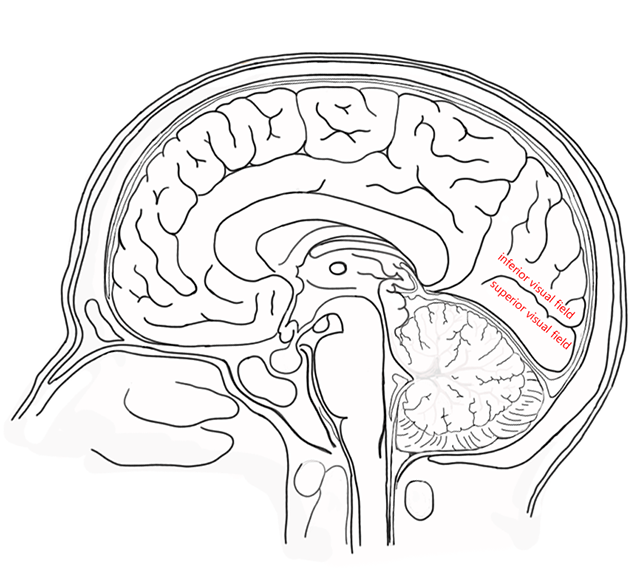
Axons from LGN cells are heavily myelinated, so they form a visible white stripe in the center of layer 4 of occipital cortex. For this reason, this area of cortex is sometimes called striate cortex (Latin stria, “stripe”). Layer 4 is divided into four sublaminae: 4A, 4B, 4Cα, and 4Cβ. Axons from magnocellular cells in the LGN end mostly in 4Cα, while axons from parvocellular cells in the LGN end mostly in 4Cβ.
Media Attributions
- Optic radiations © Gray, Henry and Spitzka, Edward Anthony is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Human Visual Pathway © Mikaela Stiver adapted by Jim Hutchins is licensed under a CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution NonCommercial NoDerivatives) license
- Calcarine sulcus © Jim Hutchins and Avalon Marker is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Upper and lower banks calcarine sulcus © Jim Hutchins and Avalon Marker is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license

