What Prehistoric and Indigenous Peoples Knew
Jim Hutchins
Objective 1: Describe the evidence that prehistoric and indigenous humans were aware of brain function.
History of Neuroscience Objective 1 Video Lecture
Neuroscience is a field that is both ineffably ancient and incredibly modern. Humans have been curious about what makes the brains work for as long as we have been human; understanding that one has a brain and trying to understand how that brain interacts with the environment is the very essence of what neuroscience and psychology define as consciousness.
Yet, as new technologies beget new tools, our understanding of the brain becomes more and more precise. Ultimately, however, as we press our knowledge to the molecular level, we find that the billions of proteins which are unique to 80 billion brain cells each connected to 10,000 other brain cells begins to challenge the limits of our understanding.
Neuroscience as a field is incredibly young amongst the sciences. The word “neuroscience” was coined in 1962 by Francis O. Schmitt. Nine years later, the first Society for Neuroscience meeting was held in Washington, DC and attracted 1,200 people. Currently, the Society for Neuroscience meetings are so large that they can only be held in three US cities: Washington, Chicago, and San Diego, and each one attracts over 30,000 attendees. In a very literal sense, neuroscientists gathered together form a small city. Neuroscience contains all the elements of the acronym STEM: science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Neuroscience has been, and will continue to be, informed by approaches from classical and quantum physics; from organic and physical chemistry; from ecology, cell biology, and molecular biology; and from the “top-down” scientific approaches of psychology.
Alison Gopnik, Andrew Melzoff, and Patricia Kuhl’s book The Scientist in the Crib reminds us that we are all born scientists. Think about the challenge for a newborn baby. It is absolutely essential for the survival of the species that a newborn human eagerly pursues two imperatives: food and shelter. Yet, armed only with our own loosely-developed brains, we must immediately figure out how to get those things within the first few seconds of life. Psychologists Harville Hendrix and Helen Hunt have made the point that these first few seconds, minutes, and days of our life will shape our entire experience of the world for a lifetime. Who is most likely to provide us with the things we need? How can we have those needs met? I am hungry; who will feed me? I am cold; who will swaddle me? If we do not get what we need, we will die. Yet, we have no experience in how to communicate those needs. We are born neuroscientists, trying to figure out how the human brain operates.
And yet. Here we are learning to be neuroscientists but at a much different level. How does the brain ensure an adequate blood supply for its needs? What part of the brain makes us recognize that a Dad Joke is funny, and prompts us to laugh (maybe a little) at it? What molecules change shape so that we can remember the smell of bread baking in our grandmother’s kitchen, even 60 or 70 years after she has transitioned? More importantly in this moment, how can I alter the shape of my brain to pass this class?
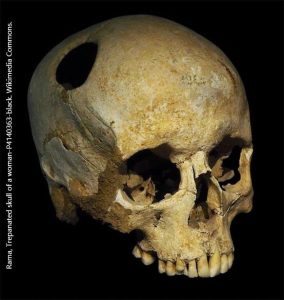
Knowing this, it should be no surprise that prehistoric cultures were struggling to figure out how human brains worked. Contrary to popular belief, they were not always wrong. In several different locations, at different times, humans figured out that if your brain begins to swell, your chances of survival were zero[1]. If an ancient shaman trepanned your skull, you were slightly more likely to survive. And so our ancestors did exactly that.
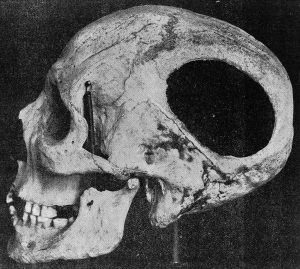
All across the globe, archaeologists have found human skulls with holes drilled or scraped in them. While humans used different technologies to create the holes in the skull, two incredible facts remain: they learned how to do it, and their patients sometimes survived. We know this because despite the surgical technique used, some (if not many) of the skulls show evidence of healing at the wound site.
 Although most of the skulls were found in European archeological digs, there was nothing special or unique about this method. In fact, one thing that argues for the “help someone recover from a head injury” vs the “cutting a hole to let out evil spirits” hypothesis is that the technique was invented independently in multiple locations. As we’d expect, the methods used were sometimes different in the Americas before the subjugation of indigenous people by European conquistadores.
Although most of the skulls were found in European archeological digs, there was nothing special or unique about this method. In fact, one thing that argues for the “help someone recover from a head injury” vs the “cutting a hole to let out evil spirits” hypothesis is that the technique was invented independently in multiple locations. As we’d expect, the methods used were sometimes different in the Americas before the subjugation of indigenous people by European conquistadores.
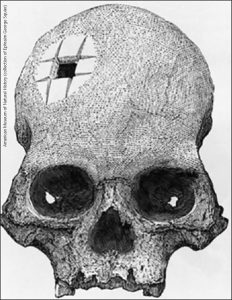
An example of the Eurocentric view of ancient trepanning is instructive. The skull shown here at left, with a set of incisions forming a square hole, was discovered at an Incan burial site and given to American archaeologist Ephraim George Squier. It shows clear evidence of wound healing. Yet the European surgeons of the mid-19th century refused to believe that Incan healers could master such a complicated surgical technique. It fell to the French neurosurgeon Paul Broca (who became famous for other reasons that we’ll discuss a few pages later) demonstrated that there are several ways to gain access to the cranial vault using stone tools. He investigated at least four techniques to gain access to the brain, using different sorts of tools and proved that indigenous peoples were almost certainly capable of this skilled surgery.
Media Attributions
- Trepanned skull Corseaux Switzerland © Rama is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Trepanned skull © Wellcome Collection is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Incan skull © The British Library is licensed under a Public Domain license
- I am presuming that an archaeological and anthropological hypothesis is correct. This is by no means proven, but it's not proveable, either. Absent a time machine, we can't know why ancient peoples cut holes in skulls. But this hypothesis is the one I find most compelling. ↵

