Golgi Tendon Organs
Caleb Bevan
Objective 6: Describe Golgi tendon organs.
Structure of a Golgi Tendon Organ
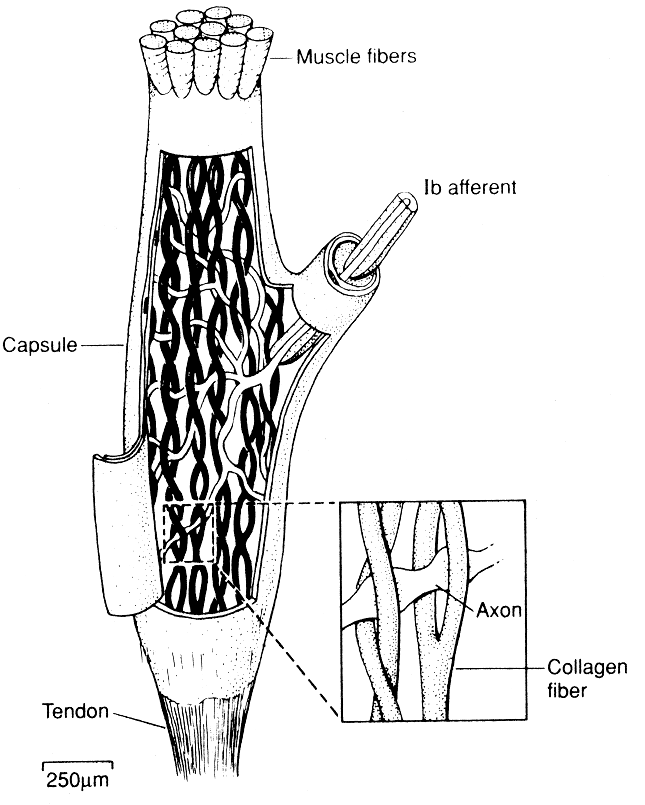
Lorem The Golgi tendon organ is an organ discovered by Camillo Golgi that senses the stretching force on a tendon connecting muscle to bone. It does this by interweaving mechanoreceptive sensory nerve endings (modified dendrites) with the collagen fibers that make up the tendon itself. The more tension on the tendon, the more the collagen fibers are stretched taut, and therefore the more action potentials are generated and travel on the spinal nerve back to the spinal cord.
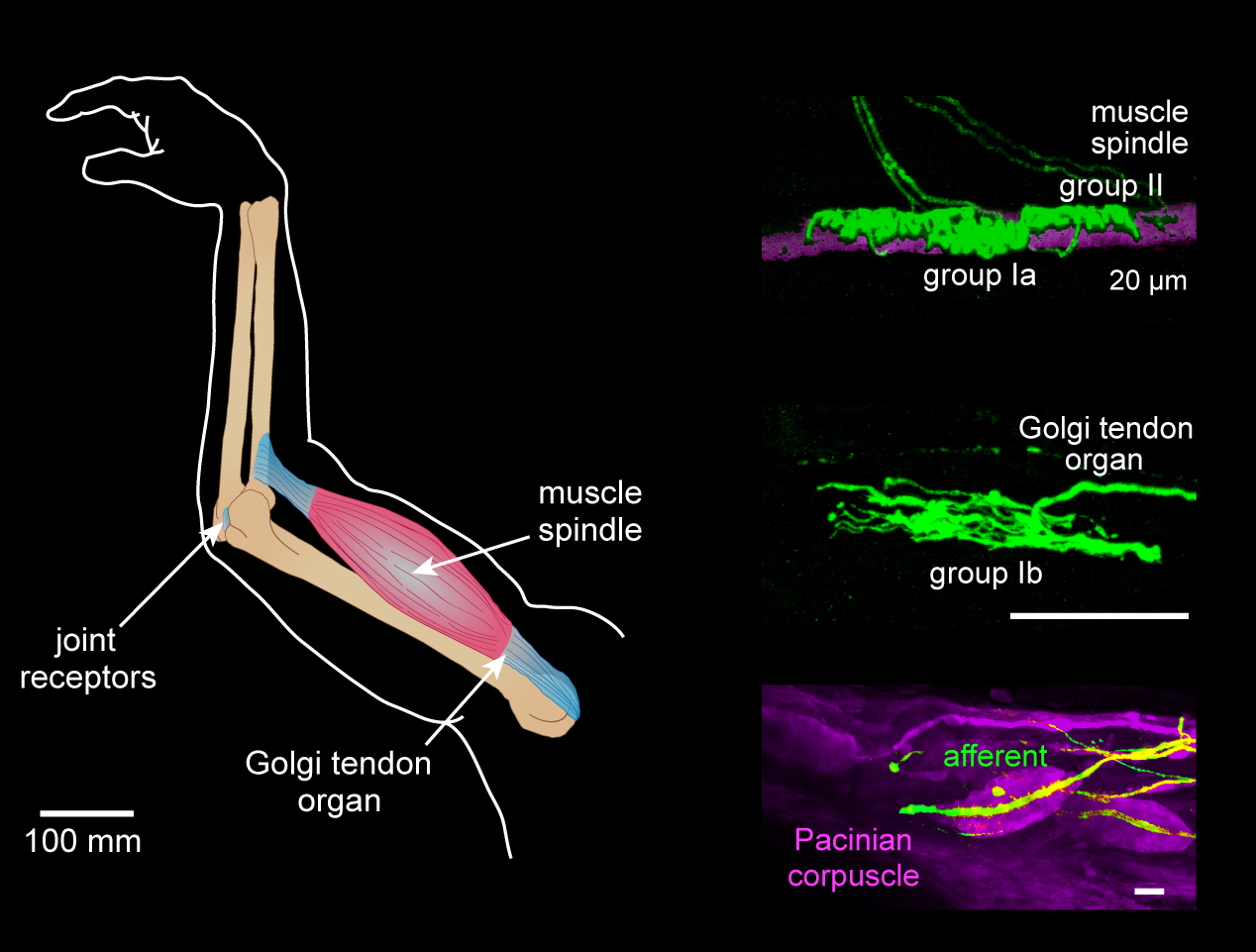
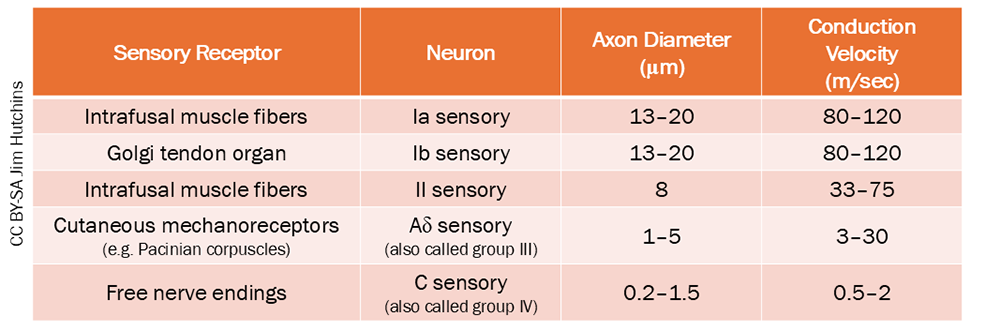
These afferent axons belong to group Ib, which are about the same diameter and conduction velocity as group Ia afferents arising from intrafusal muscle fibers.
Media Attributions
- Physiology of a Golgi tendon © David Abbink is licensed under a All Rights Reserved license
- Proprioception overview © John Tuthill is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Sensory axon diameters and conduction velocities © Jim Hutchins is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license

