Carbohydrates | Polysaccharides
Objective 3.8
3.8.1 State the monomers which make up the disaccharides.
3.8.2 Describe the different kinds of glucose polymers found in plants and animals.
Joining two monosaccharides with a dehydration synthesis reaction results in a disaccharide, a molecule with two sugars joined together. Important disaccharides are
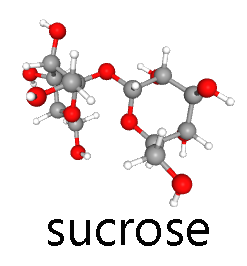
- sucrose (table sugar), which is a disaccharide made of glucose and fructose;
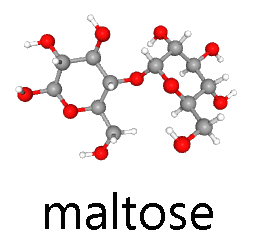
- maltose (malt sugar, glucose-glucose); and
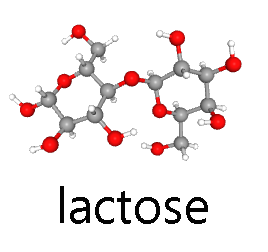
- lactose (milk sugar, glucose-galactose).
 |
 |
 |
Polysaccharides are carbohydrate polymers.
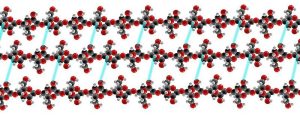
Glucose forms three kinds of large polymers which consist of chains of glucose molecules linked together by a series of dehydration synthesis reactions.
Cellulose consists of glucose in what biochemists call the β configuration and joined by β linkages. Human beings (and most other animals) don’t have the enzymes to break these. Therefore, cellulose is termed “insoluble fiber” by nutritionists. Examples of plant cell walls formed by cellulose would be the wood fibers in trees and the husks of corn plants. Humans rely on bacteria to break down cellulose (although they still can’t use this form of glucose for an energy source, the bacteria can). This has the unfortunate side effect of creating methane gas as a by-product.
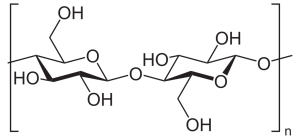
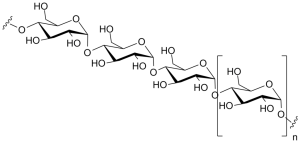
Starch is a storage form of glucose used by plants that is much more easily digested by most animals. Humans and other animals have enzymes called amylases which break down starches into α glucose molecules which can be used for energy. The two molecules which make up starch are called amylose and amylopectin.
 |
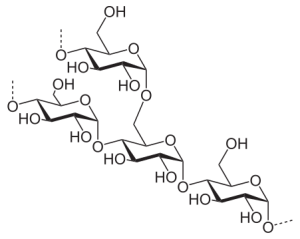 |
| amylose | amylopectin |
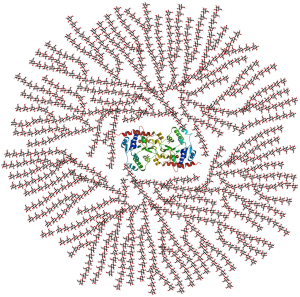
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose used by animals including humans. Glycogen, like starch, is made up of α glucose molecules joined by α linkages. This means the glycogen molecule is a ready source of stored energy. About 100 g of glycogen, representing 400 food Calories, is stored in the liver. About 400 g of glycogen (i.e. a little less than a pound), representing 1600 food Calories, is stored in the muscle. The depletion of this ready glucose reserve is a major reason that distance runners “hit the wall” when they’ve burned 2000 Calories (about 15-20 miles of running, depending on the fitness of the athlete).
Media Attributions
- U03-089 Sucrose_Conformer3D_large (1) © Hutchins, Jim is licensed under a Public Domain license
- U03-090 beta-Maltose_Conformer3D_large © Hutchins, Jim is licensed under a Public Domain license
- U03-091 beta-Lactose_Conformer3D_large © Hutchins, Jim is licensed under a Public Domain license
- U03-093 polyglucose © CeresVesta is licensed under a Public Domain license
- U03-092 polyglucose © NEUROtiker is licensed under a Public Domain license
- U03-094 amylose © glycoform is licensed under a Public Domain license
- U03-095 amylopectin © Aleksandra Kos is licensed under a Public Domain license
- U03-096 Glycogen_structure © Häggström, Mikael is licensed under a Public Domain license

