Muscular Tissue
Objective 7.12
7.12.1 Describe and identify key features of muscular tissue.
Muscle tissue is present wherever the body needs to generate force. It moves the body, maintains posture, and generates heat. Each kind of muscle tissue uses at least two cytoskeletal proteins to generate force. These are myosin and actin. Actin is the same protein that we saw as microfilaments of the cytoskeleton in Unit 5.
There are three main types of muscle tissue:
Skeletal muscle is also called voluntary muscle. The alternative name tells us that it is under our voluntary control (that is, we “choose” to use it to generate forces). It‘s also (along with cardiac, below) a type of striated muscle; it appears to be striped or striated if we look at it under a microscope. Skeletal muscle is made up of muscle cells that have fused to form a long, thin tube or myofiber called a syncytium (“joined cells”), with multiple nuclei visible on the outside of the muscle fiber
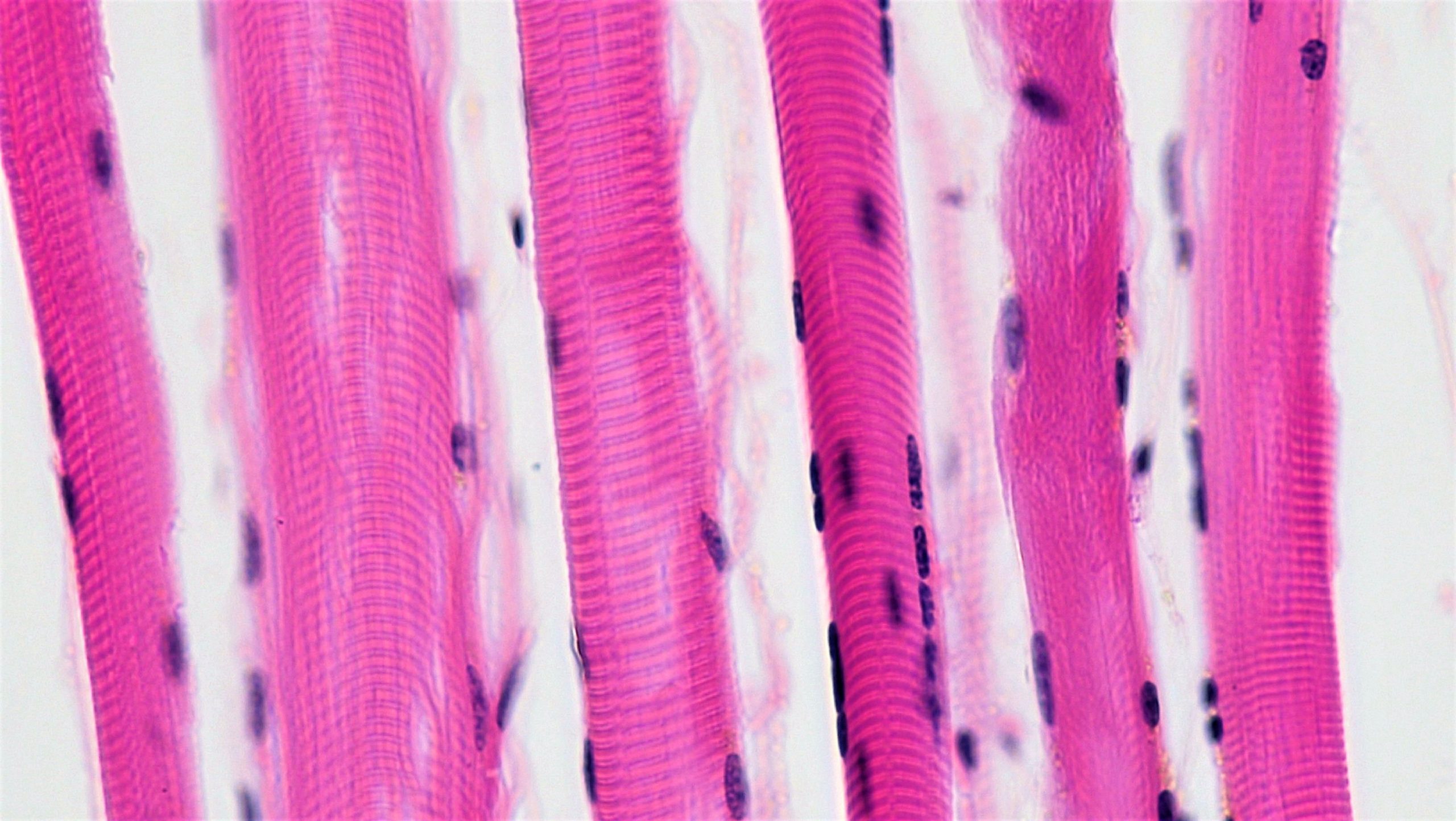
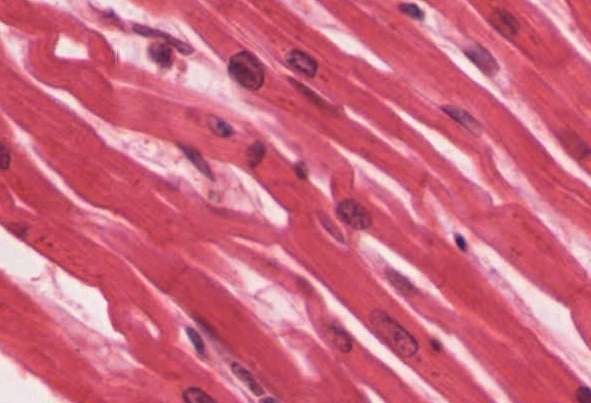
Cardiac muscle also has a striated appearance, but it is not generally thought of as being under voluntary control. The fibers are joined in branches, rather than running parallel to each other as they do in skeletal muscle. There are one or two nuclei per fiber instead of dozens. In Objective 10 we learned about desmosomes, “spot welds” that form a strong bond between cells. Cardiac muscle has those. We also learned about gap junctions which electrically couple cells. Cardiac muscle has those too. We learned about these junctions in Objective 10, and here they are in action.

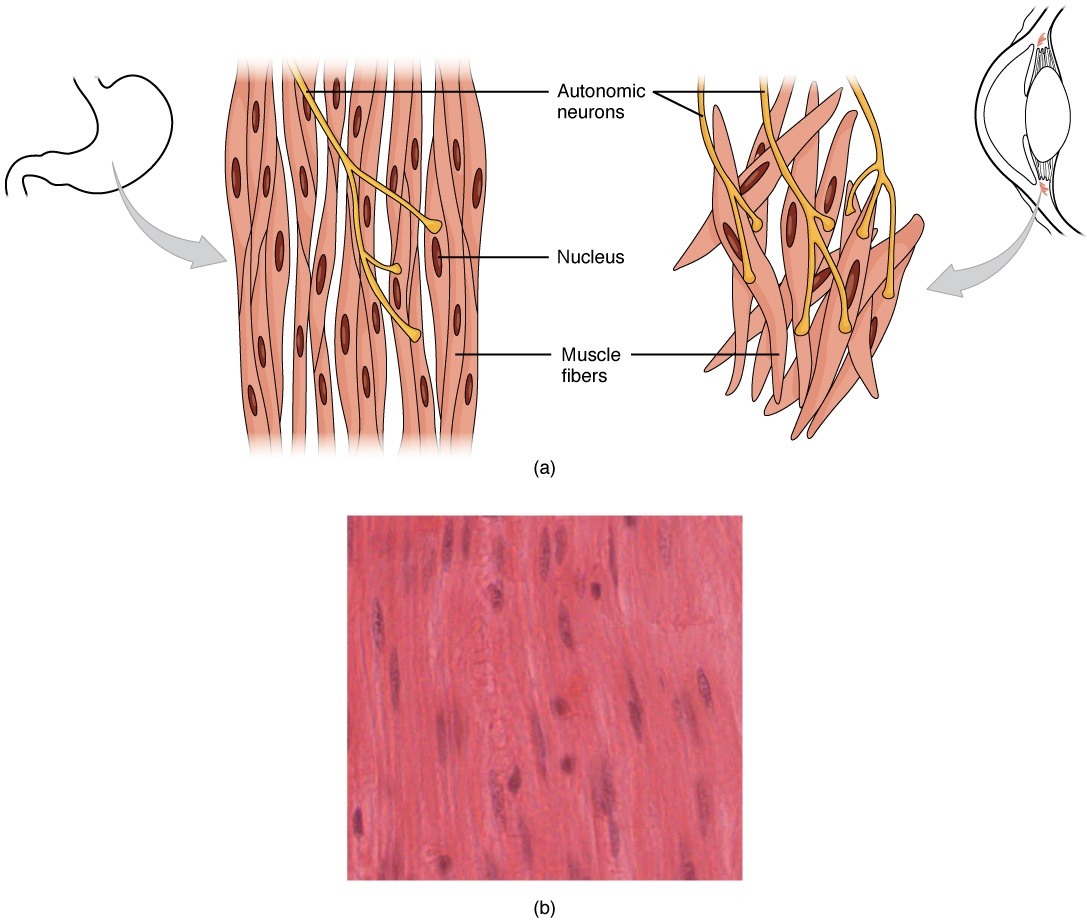
Smooth muscle is not under voluntary control. For example, the gut tube is lined with smooth muscle that keeps digestion proceeding from esophagus to anus. There are single cells, each with one nucleus, and the cytoskeleton is arranged in a random fashion so that it does not have a striated appearance.
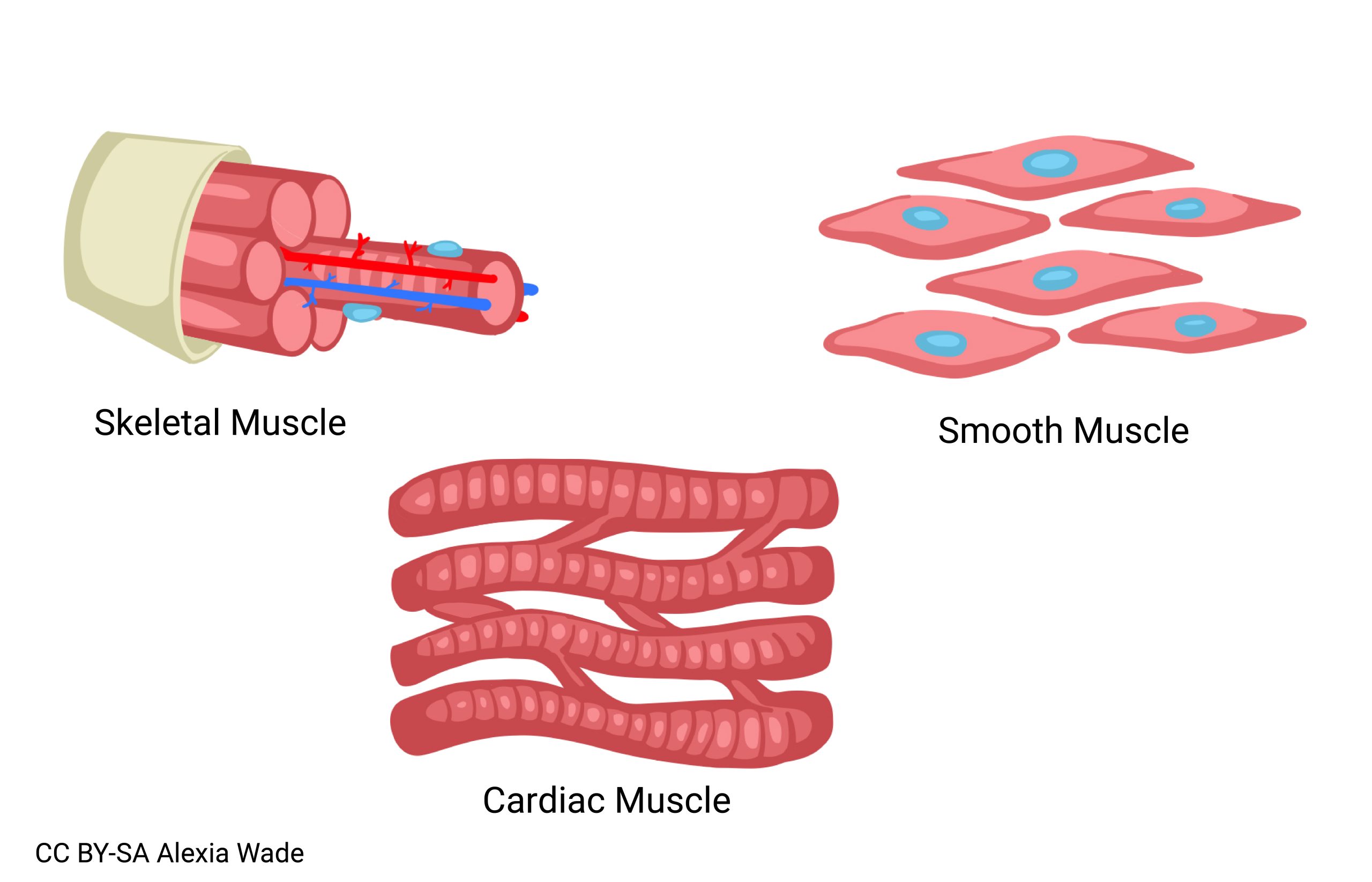
This image summarizes the three types of muscle fibers we’ve been studying.
Media Attributions
- U07-082 skeletal muscle © Berkshire Community College Bioscience is licensed under a Public Domain license
- U07-083 Cardiac_Muscle_histology © Betts, J. Gordon; Young, Kelly A.; Wise, James A.; Johnson, Eddie; Poe, Brandon; Kruse, Dean H. Korol, Oksana; Johnson, Jody E.; Womble, Mark & DeSaix, Peter is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Screenshot 2025-03-21 at 12.28.14 PM (2) © Betts, J. Gordon; Young, Kelly A.; Wise, James A.; Johnson, Eddie; Poe, Brandon; Kruse, Dean H. Korol, Oksana; Johnson, Jody E.; Womble, Mark & DeSaix, Peter is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- U07-084 Smooth Muscle © Betts, J. Gordon; Young, Kelly A.; Wise, James A.; Johnson, Eddie; Poe, Brandon; Kruse, Dean H. Korol, Oksana; Johnson, Jody E.; Womble, Mark & DeSaix, Peter is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- U07-085 muscle types © Wade, Alexia is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license

