Lipid Signaling Molecules
Objective 3.6
3.6.1 Recognize the lipids which are used as signaling molecules: steroids and eicosanoids, including arachidonic acid.
3.6.2 Name some examples of each class.
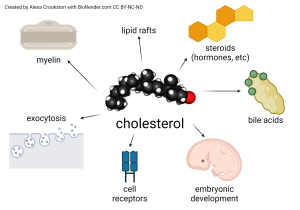
An important group of signaling molecules in the human body are lipids. The first of these are the steroids. We’ve already seen that estrogen, testosterone, and the stress hormone cortisol are based on the cholesterol structure (i.e. are steroids). So we already discovered the first major set of lipid signaling molecules in the human body.
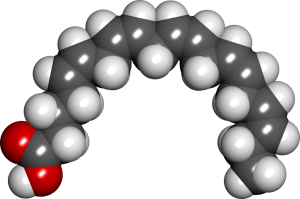 Another class which is less known but no less important are those with 20 carbons called eicosanoids. (The prefix eicosa– means “twenty” in Greek.) Eicosanoids tend to have lots of double bonds, and therefore lots of kinks, so many that they double back on themselves in a curled structure.
Another class which is less known but no less important are those with 20 carbons called eicosanoids. (The prefix eicosa– means “twenty” in Greek.) Eicosanoids tend to have lots of double bonds, and therefore lots of kinks, so many that they double back on themselves in a curled structure.
Prostaglandins are an important group of eicosanoids. The synthesis of one of these, prostaglandin E2, is catalyzed by enzymes called cyclo-oxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2); note the –ase enzyme name ending). These COX enzymes are blocked by aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs). “Non-steroidal” is a reference to the fact these molecules aren’t cortisol, which is the steroid signaling molecule we saw earlier that blocks the immune response, among other actions. Prostaglandins, therefore, are eicosanoids released as part of the body’s inflammatory response.
Leukotrienes are another important class of eicosanoid inflammatory signaling molecules. Blocking these is an important part of most asthma therapeutic regimens.
Blocking these is an important part of most asthma therapeutic regimens and an alternative to antihistamines for treating allergies.
Arachidonic acid is technically an eicosanoid but most biochemists place it in a separate category. The most important arachidonic acid derivative in the human body is a signaling molecule called anandamide, which is released in situations of moderate stress and reduces the body’s response to pain and modifies mood. Anandamide is a naturally occurring (endogenous) signaling molecule. The psychoactive ingredient in cannabis, Δ9-tetrahydrocannibinol or THC, binds to the same receptor on nerve cells as does anandamide.
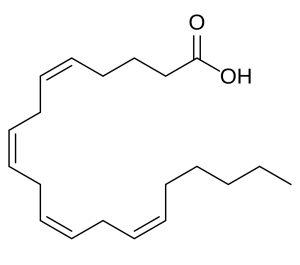 |
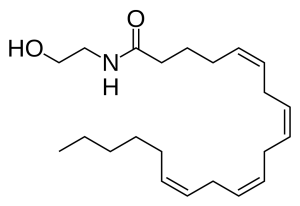 |
| arachidonic acid | anandamide |
Media Attributions
- U03-073 Cholesterol © Crookston, Alexa is licensed under a CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution NonCommercial NoDerivatives) license
- U03-074 Eicosapentaenoic_acid_spacefill © SubDural12 is licensed under a Public Domain license
- U03-075 arachidonic acid © Edward the Confessor is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- U03-076 anandamide © Fvasconcellos is licensed under a Public Domain license

