43 Overview of Photosynthesis
Jung Choi; Mary Ann Clark; and Matthew Douglas
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
- Explain the significance of photosynthesis to other living organisms
- Describe the main structures involved in photosynthesis
- Identify the substrates and products of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, or the process in which plants and some other living organisms transform light energy into chemical energy, is essential to all life on earth; both plants and animals depend on it. It is the only biological process that can capture energy that originates from sunlight and converts it into chemical compounds (carbohydrates) that every organism uses to power its metabolism. It is also a source of oxygen necessary for many living organisms. In brief, the energy of sunlight is “captured” to energize electrons, whose energy is then stored in the covalent bonds of sugar molecules. How long lasting and stable are those covalent bonds? The energy extracted today by the burning of coal and petroleum products represents sunlight energy captured and stored by photosynthesis 350 to 200 million years ago during the Carboniferous Period.
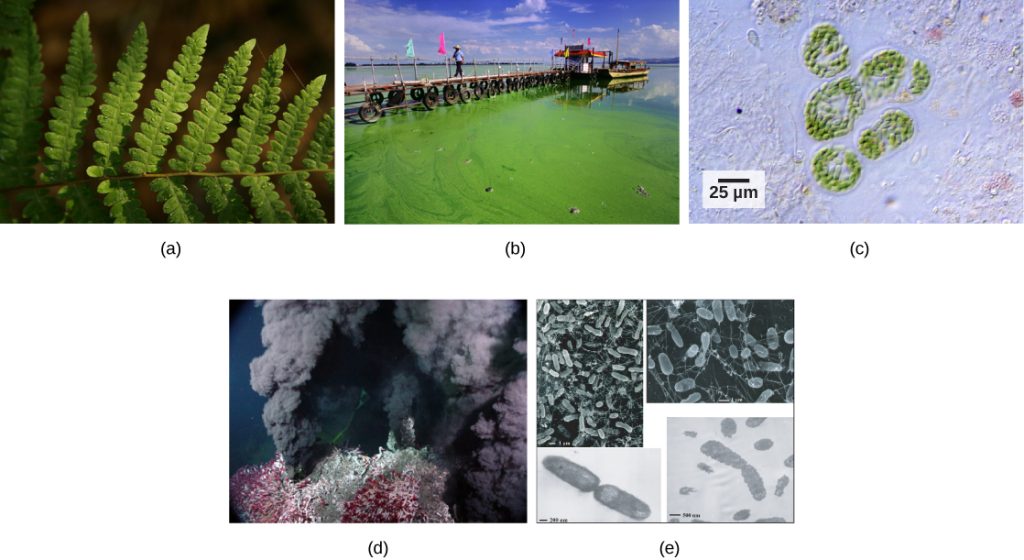
Plants, algae, and a group of bacteria called cyanobacteria are the only organisms capable of performing photosynthesis (Figure 8.2). Because they use light to manufacture their own food, they are called photoautotrophs (literally, “self-feeders using light”). Other organisms, such as animals, fungi, and most other bacteria, are termed heterotrophs (“other feeders”), because they must rely on the sugars produced by photosynthetic organisms for their energy needs. A third very interesting group of bacteria synthesize sugars, not by using sunlight’s energy, but by extracting energy from inorganic chemical compounds. For this reason, they are referred to as chemoautotrophs.
The importance of photosynthesis is not just that it can capture sunlight’s energy. After all, a lizard sunning itself on a cold day can use the sun’s energy to warm up in a process called behavioral thermoregulation. In contrast, photosynthesis is vital because it evolved as a way to store the energy from solar radiation (the “photo-” part) to energy in the carbon-carbon bonds of carbohydrate molecules (the “-synthesis” part). Those carbohydrates are the energy source that heterotrophs use to power the synthesis of ATP via respiration. Therefore, photosynthesis powers 99 percent of Earth’s ecosystems. When a top predator, such as a wolf, preys on a deer (Figure 8.3), the wolf is at the end of an energy path that went from nuclear reactions on the surface of the sun, to visible light, to photosynthesis, to vegetation, to deer, and finally to the wolf.

Main Structures and Summary of Photosynthesis
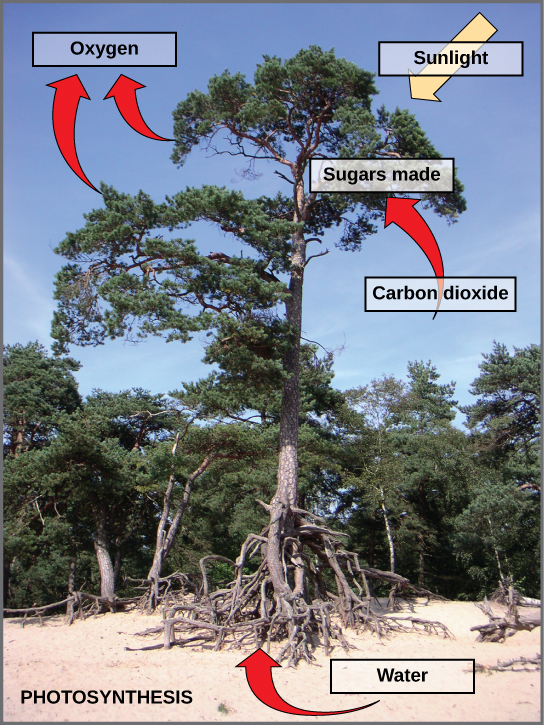
Photosynthesis is a multi-step process that requires specific wavelengths of visible sunlight, carbon dioxide (which is low in energy), and water as substrates (Figure 8.4). After the process is complete, it releases oxygen and produces glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), as well as simple carbohydrate molecules (high in energy) that can then be converted into glucose, sucrose, or any of dozens of other sugar molecules. These sugar molecules contain energy and the energized carbon that all living things need to survive.
The following is the chemical equation for photosynthesis (Figure 8.5):
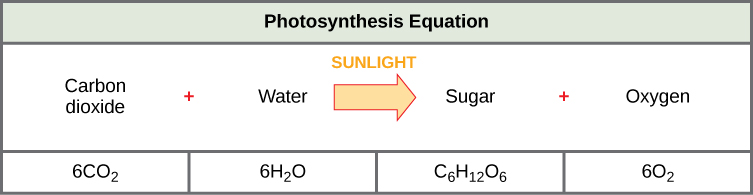
Although the equation looks simple, the many steps that take place during photosynthesis are actually quite complex. Before learning the details of how photoautotrophs turn sunlight into food, it is important to become familiar with the structures involved.
Basic Photosynthetic Structures
In plants, photosynthesis generally takes place in leaves, which consist of several layers of cells. The process of photosynthesis occurs in a middle layer called the mesophyll. The gas exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen occurs through small, regulated openings called stomata (singular: stoma), which also play roles in the regulation of gas exchange and water balance. The stomata are typically located on the underside of the leaf, which helps to minimize water loss due to high temperatures on the upper surface of the leaf. Each stoma is flanked by guard cells that regulate the opening and closing of the stomata by swelling or shrinking in response to osmotic changes.
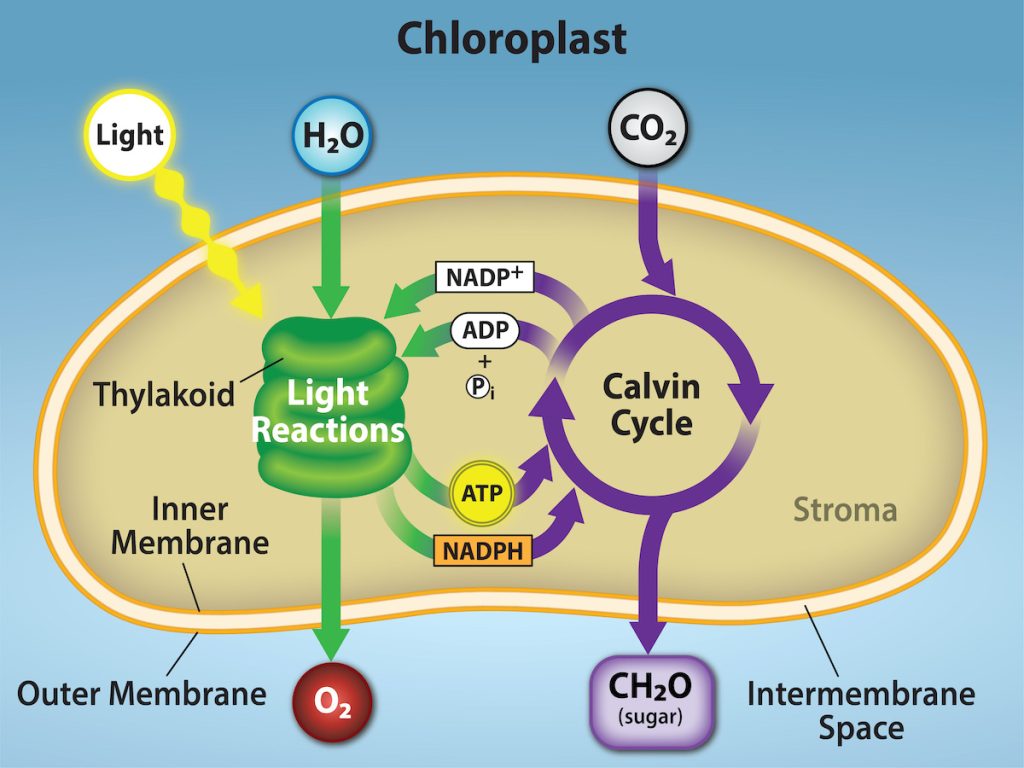
In all autotrophic eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place inside an organelle called a chloroplast. For plants, chloroplast-containing cells exist mostly in the mesophyll. Chloroplasts have a double membrane envelope (composed of an outer membrane and an inner membrane), and are ancestrally derived from ancient free-living cyanobacteria. Within the chloroplast are stacked, disc-shaped structures called thylakoids. Embedded in the thylakoid membrane is chlorophyll, a pigment (molecule that absorbs light) responsible for the initial interaction between light and plant material, and numerous proteins that make up the electron transport chain. The thylakoid membrane encloses an internal space called the thylakoid lumen. As shown in Figure 8.6, a stack of thylakoids is called a granum, and the liquid-filled space surrounding the granum is called stroma or “bed” (not to be confused with stoma or “mouth,” an opening on the leaf epidermis).
The Two Parts of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in two sequential stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions. In the light-dependent reactions, energy from sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll and that energy is converted into stored chemical energy. In the light-independent reactions, the chemical energy harvested during the light-dependent reactions drives the assembly of sugar molecules from carbon dioxide. Therefore, although the light-independent reactions do not use light as a reactant, they require the products of the light-dependent reactions to function. In addition, however, several enzymes of the light-independent reactions are activated by light. The light-dependent reactions utilize certain molecules to temporarily store the energy: These are referred to as energy carriers. The energy carriers that move energy from light-dependent reactions to light-independent reactions can be thought of as “full” because they are rich in energy. After the energy is released, the “empty” energy carriers return to the light-dependent reaction to obtain more energy. Figure 8.7 illustrates the components inside the chloroplast where the light-dependent and light-independent reactions take place.
Link to Learning
Click the link to learn more about photosynthesis.
Everyday Connection
Photosynthesis at the Grocery Store



