65 DNA Structure
Jung Choi; Mary Ann Clark; and Matthew Douglas
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:
- Describe the structure of DNA
- Explain the Sanger method of DNA sequencing
- Discuss the similarities and differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA
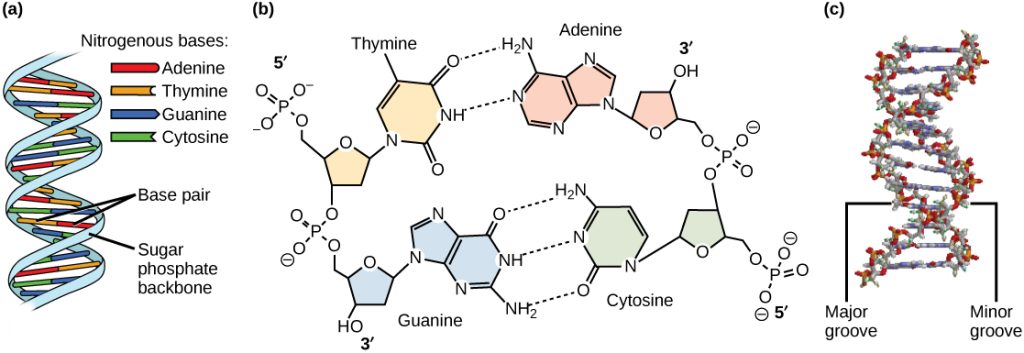
The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. The important components of the nucleotide are a nitrogenous (nitrogen-bearing) base, a 5-carbon sugar (pentose), and a phosphate group (Figure 14.5). The nucleotide is named depending on the nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base can be a purine such as adenine (A) and guanine (G), or a pyrimidine such as cytosine (C) and thymine (T).
Visual Connection
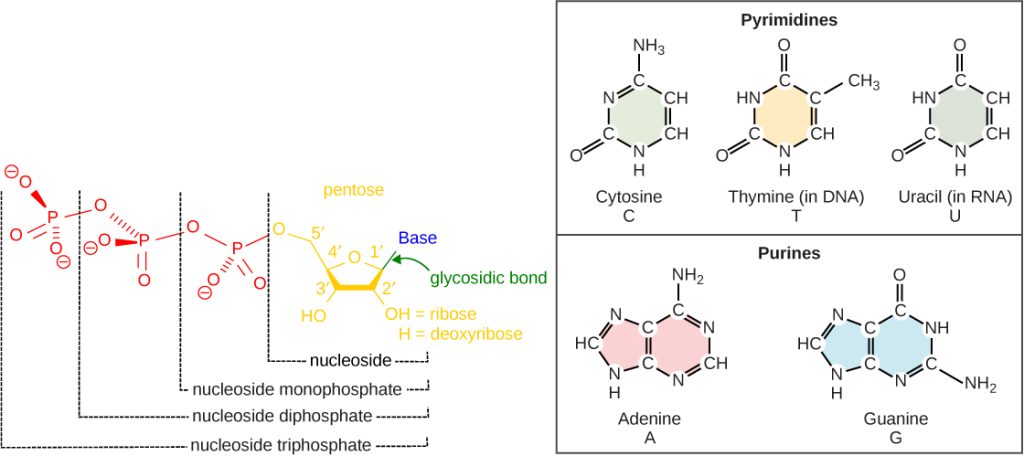
The purines have a double ring structure with a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring. Pyrimidines are smaller in size; they have a single six-membered ring structure.
The sugar is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. The carbon atoms of the five-carbon sugar are numbered 1′, 2′, 3′, 4′, and 5′ (1′ is read as “one prime”). The phosphate, which makes DNA and RNA acidic, is connected to the 5′ carbon of the sugar by the formation of an ester linkage between phosphoric acid and the 5′-OH group (an ester is an acid + an alcohol). In DNA nucleotides, the 3′ carbon of the sugar deoxyribose is attached to a hydroxyl (OH) group. In RNA nucleotides, the 2′ carbon of the sugar ribose also contains a hydroxyl group. The base is attached to the 1’carbon of the sugar.
The nucleotides combine with each other to produce phosphodiester bonds. The phosphate residue attached to the 5′ carbon of the sugar of one nucleotide forms a second ester linkage with the hydroxyl group of the 3′ carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide, thereby forming a 5′-3′ phosphodiester bond. In a polynucleotide, one end of the chain has a free 5′ phosphate, and the other end has a free 3′-OH. These are called the 5′ and 3′ ends of the chain.
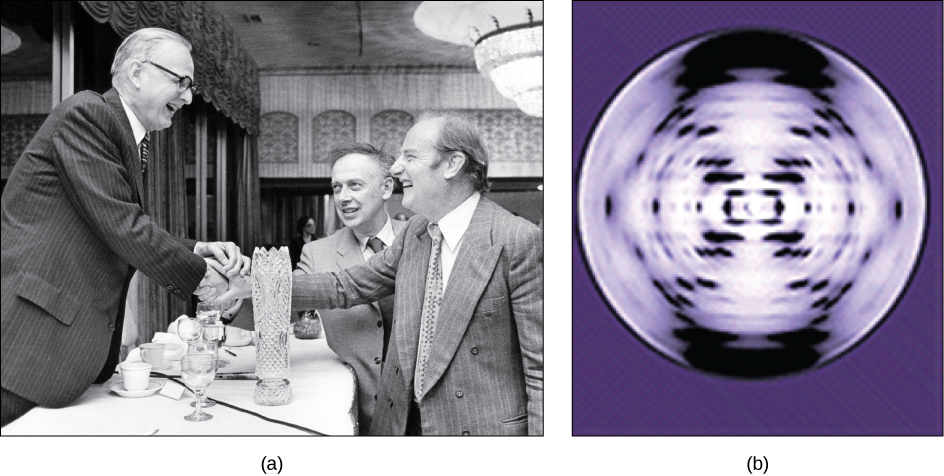
Rosalind Franklin joined the scientists at the Medical Research Unit, King’s College when John Randall recruited her to work on the structure of DNA. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) was originally discovered in 1898 by Johann Miescher, and it was known that it was a key to genetics. But it was not until the middle of the 20th century when scientific methods had developed to where the actual structure of the molecule could be discovered, and Rosalind Franklin’s work was key to that methodology.
Rosalind Franklin worked on the DNA molecule from 1951 until 1953. Using x-ray crystallography, she took photographs of the B version of the molecule. A co-worker with whom Franklin did not have a good working relationship, Maurice H.F. Wilkins, showed Franklin’s photographs of DNA to James Watson—without Franklin’s permission. Watson and his research partner Francis Crick were working independently on the structure of DNA, and Watson realized that these photographs were the scientific evidence they needed to prove that the DNA molecule was a double-stranded helix.


In the 1950s, Francis Crick and James Watson worked together to determine the structure of DNA at the University of Cambridge, England. Other scientists like Linus Pauling and Maurice Wilkins were also actively exploring this field. Pauling previously had discovered the secondary structure of proteins using X-ray crystallography. In Wilkins’ lab, researcher Rosalind Franklin was using X-ray diffraction methods to understand the structure of DNA. Watson and Crick were able to piece together the puzzle of the DNA molecule on the basis of Franklin’s data because Crick had also studied X-ray diffraction (Figure 14.6). In 1962, James Watson, Francis Crick, and Maurice Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine. Unfortunately, by then Franklin had died, and Nobel prizes are not awarded posthumously.
Watson and Crick proposed that DNA is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other to form a right-handed helix. Base pairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine on opposite strands, so that A pairs with T, and G pairs with C (suggested by Chargaff’s Rules). Thus, adenine and thymine are complementary base pairs, and cytosine and guanine are also complementary base pairs. The base pairs are stabilized by hydrogen bonds: adenine and thymine form two hydrogen bonds and cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds. The two strands are anti-parallel in nature; that is, the 3′ end of one strand faces the 5′ end of the other strand. The sugar and phosphate of the nucleotides form the backbone of the structure, whereas the nitrogenous bases are stacked inside, like the rungs of a ladder. Each base pair is separated from the next base pair by a distance of 0.34 nm, and each turn of the helix measures 3.4 nm. Therefore, 10 base pairs are present per turn of the helix. The diameter of the DNA double-helix is 2 nm, and it is uniform throughout. Only the pairing between a purine and pyrimidine and the antiparallel orientation of the two DNA strands can explain the uniform diameter. The twisting of the two strands around each other results in the formation of uniformly spaced major and minor grooves (Figure 14.7).