17 The Experience Economy
The Experience Economy: From Memorable Moments to Transformative Journeys
In 1998, B. Joseph Pine II and James H. Gilmore introduced the concept of the Experience Economy in a groundbreaking Harvard Business Review article. This new economic model represented a significant shift in how businesses create value for consumers, marking the next stage in the evolution of economic value.
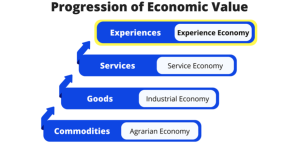
The progression from an agrarian economy to an industrial economy, and then to a service economy, set the stage for the emergence of the Experience Economy. In this new paradigm, businesses move beyond delivering services to staging memorable events for their customers, with the memory itself becoming the product.
Source: https://www.selectgroup.com/client-solutions/client-blog/thrive-experience-economy/
The Experience Economy differs fundamentally from the service economy. While the service economy focuses on delivering intangible benefits efficiently, the Experience Economy is about creating personal, memorable events that engage customers on emotional, physical, intellectual, or even spiritual levels. This shift represents a new source of value creation and competitive advantage for businesses across various sectors.
Core Principles of the Experience Economy
Experiences as Distinct Economic Offerings
In the Experience Economy, experiences emerge as a distinct economic offering, separate from services just as services are distinct from goods. Experiences are inherently personal, existing only in the mind of an individual who has been engaged on multiple levels. They are memorable, revealing themselves over time, and often transformative.
For example, a coffee shop doesn’t just sell coffee (a good) or the service of preparing and serving that coffee. In the Experience Economy, it might create a complete sensory experience around coffee consumption, from the aroma that greets customers at the door to the storytelling about coffee origins, to the ritualistic preparation methods – all culminating in a memorable “coffee experience” that transcends the simple act of drinking a beverage.
Staging Experiences vs. Delivering Services
The key difference between delivering services and staging experiences lies in the level of engagement and the lasting impact on the customer. While services are about what you do for the customer, experiences are about how you make the customer feel.
Staging an experience involves carefully choreographing a series of events that engage the customer in a personal way. This requires businesses to think like theatrical producers, considering every aspect of the customer interaction as part of a cohesive performance. For example, a theme restaurant doesn’t just serve food; it creates an immersive environment where the decor, staff behavior, menu design, and even the names of dishes all contribute to a unified theme that transports the diner to another world.
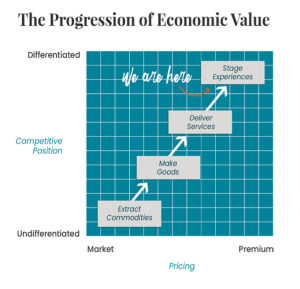
The Progression of Economic Value
The progression of economic value moves from extracting commodities to making goods to delivering services to staging experiences. Each step in this progression results in a higher level of differentiation and, consequently, a higher price point.
Source: https://insights.weareeverise.com/rise-of-experience-economy
In the Experience Economy, businesses can charge admission for the experience itself, not just for the goods or services provided. This is evident in the premium prices people are willing to pay for experiential offerings like themed restaurants, interactive museums, or immersive theater productions.
For example, consider how a simple birthday party has evolved through this progression:
- Commodity: Parents buy ingredients to bake a cake (low cost)
- Good: Parents buy a pre-made cake from a store (slightly higher cost)
- Service: Parents hire a party planner to organize the event (higher cost)
- Experience: Parents pay for an all-inclusive, themed birthday experience at a specialized venue (highest cost)

Source: https://www.exhibitoronline.com/corpevent/article.asp?ID=745
This progression illustrates how experiences command a premium in the market, reflecting their higher perceived value to consumers.
The Four Realms of Experience and Their Dimensions
Immersion and Absorption in Experiences
Immersion refers to the state of being physically (or virtually) surrounded by an experience. It’s about becoming part of the experience environment. For example, when you visit a theme park, you’re immersed in a carefully crafted world that engages all your senses.
Absorption, on the other hand, is the state of having one’s attention completely engaged by an experience. It’s about taking the experience into yourself. When you’re engrossed in a captivating movie or book, you’re in a state of absorption.
Passive vs. Active participation:
Passive participation occurs when the customer does not directly affect or influence the performance of the experience. They are observers or listeners, like audience members at a symphony concert.
Active participation involves the customer playing a key role in creating the performance or event that yields the experience. Interactive art installations, escape rooms, or hands-on cooking classes are examples of experiences that require active participation.
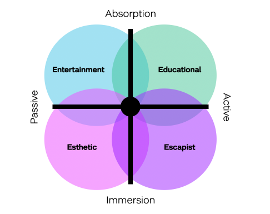
The Experience Realms Grid
To better understand and categorize different types of experiences, we can place them on a two-dimensional grid. This grid, introduced by Pine and Gilmore, helps visualize how different experiences relate to one another and how they engage participants.
The grid is structured as follows:
- The vertical axis represents the level of customer participation, ranging from passive at the bottom to active at the top.
- The horizontal axis represents the type of connection, or environmental relationship, that unites customers with the event or performance. This ranges from absorption on the left to immersion on the right.
This creates four quadrants, each representing a distinct realm of experience:
- Entertainment (Passive Absorption)
- Educational (Active Absorption)
- Esthetic (Passive Immersion)
- Escapist (Active Immersion)
Source: https://jenbonhomme.medium.com/the-experience-economy-83fe7a26a594
Entertainment (Absorption – Passive)
Entertainment experiences are those that are passively absorbed through the senses. These are typically enjoyable experiences that do not require active participation from the audience. Examples include watching a movie, attending a concert, or viewing a dance performance.
In the entertainment realm, businesses focus on creating captivating content that can hold the audience’s attention and evoke emotional responses. The challenge is to make the experience memorable enough that it stands out in a world saturated with entertainment options.
Educational (Absorption – Active)
Educational experiences actively engage the mind or body to increase knowledge or skills. These experiences require the active participation of the individual to absorb the intended lessons or develop new abilities. Examples include attending a workshop, participating in a wine tasting class, or engaging with an interactive museum exhibit.
In designing educational experiences, businesses must balance information delivery with engagement techniques to ensure that learning is both effective and enjoyable. The rise of “edutainment” – educational entertainment – is a direct result of this approach.
Esthetic (Immersion – Passive)
Esthetic experiences immerse individuals in an environment but allow them to remain passive. These experiences are about being there, soaking in the atmosphere without necessarily doing anything. Visiting an art gallery, enjoying a scenic viewpoint, or relaxing in a beautifully designed spa are examples of esthetic experiences.
The key to creating powerful esthetic experiences lies in attention to detail in the environment. Every element should contribute to the desired atmosphere and emotional response.
Escapist (Immersion – Active)
Escapist experiences involve both active participation and immersion. These are the experiences that transport participants to a different time, place, or reality, requiring them to play an active role in shaping the experience. Examples include participating in a virtual reality game, acting in an interactive theater production, or engaging in extreme sports.
Escapist experiences offer the deepest level of immersion and often the most memorable outcomes. They challenge businesses to create comprehensive alternate realities that participants can fully engage with.
Sweet Spot: Combining All Four Realms
The most compelling experiences incorporate elements from all four realms, creating a “sweet spot” in the center of the experience domains. By blending aspects of entertainment, education, esthetics, and escapism, businesses can create rich, multifaceted experiences that appeal to a wide range of preferences and engage customers on multiple levels.
For instance, a historical reenactment village might offer:
- Entertainment through performances and storytelling
- Education about historical facts and lifestyles
- Esthetic immersion in accurately recreated historical environments
- Escapist elements by allowing visitors to dress in period costumes and participate in daily activities of the era
Strategies for Enhancing Immersion and Absorption in Experiences
To create more engaging and memorable experiences, businesses can employ several strategies:
- Use multisensory elements: Engage all five senses to increase immersion. A restaurant might use not just taste and smell, but also carefully designed lighting, background music, and textured furniture to create a fully immersive dining experience.
- Create opportunities for active participation: Even in primarily passive experiences, find ways to involve the audience. A concert might include moments of audience sing-alongs or interactive light shows controlled by audience movements.
- Design environments that facilitate flow states: Create experiences that balance challenge and skill level to promote a state of full immersion and focus. This is particularly relevant for educational and escapist experiences.
- Utilize storytelling: Weave a narrative throughout the experience to enhance emotional engagement and create a cohesive journey for the participant.
- Leverage technology: Use AR, VR, or mobile apps to augment real-world experiences, providing additional layers of information or interactivity.
- Theme the Experience: Develop a well-defined theme that resonates throughout all aspects of the experience.
- Harmonize Impressions with Positive Cues: Ensure that every element of the experience supports the theme and leaves a positive impression.
- Eliminate Negative Cues: Remove any aspects that detract from or contradict the intended experience.
- Mix in Memorabilia: Offer tangible items that serve as physical reminders of the experience.
The Transformation Economy: Beyond Experiences
The Transformation Economy represents the next evolutionary step beyond the Experience Economy. In this new paradigm, the focus shifts from staging memorable experiences to facilitating personal transformations. This concept suggests that consumers are increasingly seeking experiences that change them in meaningful and lasting ways.
In the Transformation Economy, businesses don’t just create memorable events; they guide customers through a process of personal growth and development. The product is no longer just the experience itself, but the improved customer that results from the experience. This shift represents a profound change in how businesses create value and interact with their customers.
Evolution from Experience Economy to Transformation Economy
The transition from the Experience Economy to the Transformation Economy is driven by several factors:
- Saturation of experiences: As memorable experiences become more commonplace, consumers seek deeper, more meaningful engagements.
- Increased focus on personal growth: There’s a growing cultural emphasis on self-improvement and personal development.
- Rise of the wellness industry: The booming wellness sector has primed consumers to seek transformative experiences in various aspects of their lives.
- Technology enabling personalization: Advanced data analytics and AI allow businesses to tailor transformative experiences to individual needs and goals.
Key Characteristics of Transformational Experiences
- Intensely personal: Transformational experiences are tailored to the individual’s specific needs, goals, and current state. They often involve deep self-reflection and personal challenge.
- Requires active and interested consumers: Unlike passive experiences, transformational experiences demand high levels of engagement and commitment from participants. Consumers must be willing to put in effort and potentially face discomfort for growth.
- Brand’s willingness to adapt and be part of the shift: Companies must be prepared to evolve alongside their customers, continually refining their offerings based on customer feedback and outcomes.
- Long-term engagement: Transformation is often a lengthy process, requiring sustained interaction between the business and the customer over time.
- Clear outcomes and measurable results: Transformational experiences should have defined goals and ways to track progress, allowing customers to see their growth.
Examples of Companies in the Transformation Economy
- SoulCycle: This fitness company has transformed the concept of indoor cycling into a spiritual and emotional journey. Classes are designed not just to improve physical fitness, but to boost confidence, reduce stress, and foster a sense of community. The experience is carefully crafted, from the inspirational instructors to the curated playlists, all aimed at facilitating personal transformation.
- CrossFit: More than just a fitness regimen, CrossFit has created a global community centered around personal growth and transformation. The program challenges participants physically and mentally, fostering resilience and self-efficacy. The community aspect plays a crucial role, with members supporting each other’s transformative journeys.
- MindValley: This online education platform offers courses and retreats focused on personal development across various life domains. MindValley’s approach combines cutting-edge learning techniques with community support and immersive experiences. Their offerings range from online courses to transformational retreats in exotic locations, all designed to facilitate deep personal growth.
- WeightWatchers: Originally a weight loss company, WeightWatchers has evolved to focus on overall wellness transformation. Their program now includes not just nutrition guidance, but also fitness, mindfulness, and community support, aiming for holistic life changes rather than just weight loss.
The Role of Self-Actualization
Transformational experiences often target the highest level of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs: self-actualization. This concept refers to the realization of one’s full potential and the ongoing pursuit of personal growth.
In the Transformation Economy, businesses position themselves as facilitators of self-actualization, appealing to consumers’ deep-seated desires for personal growth and fulfillment. This approach taps into powerful motivations that go beyond mere consumption or entertainment, creating strong emotional connections between brands and consumers.
Creating Meaningful and Transformational Experiences
Moving Beyond Memorable to Meaningful
To transition from memorable to meaningful experiences, businesses must:
- Align experiences with customers’ values and beliefs: This requires deep understanding of target audiences and their core motivations.
- Create opportunities for reflection: Meaningful experiences often involve moments of insight or realization. Businesses can facilitate this by building in opportunities for customers to reflect on their experiences.
- Foster connections: Meaningful experiences often involve connecting with others who share similar values or goals. Creating community around the experience can enhance its significance.
- Emphasize purpose: Framing the experience within a larger context of purpose or social impact can increase its perceived meaningfulness.
Designing for Transformation
Understanding customer journeys:
-
- Conduct thorough research to map out the entire customer experience, from initial awareness to post-experience follow-up.
- Identify key touchpoints and moments of truth where transformative interventions can have the most impact.
- Use data analytics and customer feedback to continually refine and improve the journey map.
Facilitating personal growth and change:
-
- Develop a clear framework or methodology for guiding customers through their transformative journey.
- Provide tools, resources, and support systems to help customers overcome obstacles and achieve their goals.
- Incorporate elements of coaching or mentorship to provide personalized guidance.
- Create a supportive community environment where customers can share experiences and motivate each other.
Measuring transformation outcomes:
-
- Define clear, measurable objectives for the desired transformation.
- Implement systems to track customer progress over time, such as regular check-ins or assessments.
- Use both quantitative metrics (e.g., weight lost, skills acquired) and qualitative measures (e.g., testimonials, self-reported well-being) to gauge transformation.
- Celebrate milestones and achievements to reinforce progress and motivate continued engagement.
Conclusion
The Experience Economy has evolved from simply staging memorable events to facilitating transformative journeys. As businesses adapt to this shift, they must focus on creating experiences that not only engage customers on multiple levels but also contribute to their personal growth and self-actualization. The progression from commodity to goods to services to experiences, and now to transformations, represents a continual increase in economic value and customer engagement. Companies that successfully navigate this transition will be well-positioned to create deep, lasting connections with their customers, driving loyalty and sustained success in an increasingly competitive marketplace. By understanding the four realms of experience, leveraging strategies for enhancing immersion and absorption, and designing for meaningful transformation, businesses can create offerings that resonate deeply with consumers’ desires for personal growth and fulfillment.
Appendix: Examples of Organizations Utilizing Experience Economy Principles
Disney Parks and Resorts
Disney is a prime example of a company that masterfully applies Experience Economy principles across all four realms:
- Entertainment: Spectacular shows, parades, and character interactions
- Educational: Interactive exhibits and workshops teaching about animation, nature, and technology
- Esthetic: Immersive, detailed theming in every area of the parks
- Escapist: Role-playing experiences like Star Wars: Galaxy’s Edge, where visitors become part of the story
Disney also facilitates transformations through programs like Disney Institute, which offers professional development experiences based on Disney’s business insights.
Enhancing Immersion:
- Detailed theming: Every aspect of the environment, from architecture to soundscapes, is designed to transport visitors to different worlds or time periods.
- Cast member interactions: Employees stay in character, reinforcing the illusion of being in a different reality.
- Multisensory experiences: Attractions like Soarin’ Around the World use sight, sound, motion, and even scent to create a fully immersive experience.
Enhancing Absorption:
- Storytelling: Rides and attractions are built around compelling narratives that capture visitors’ attention.
- Hidden details: “Hidden Mickeys” and other subtle design elements encourage guests to pay close attention to their surroundings.
- Educational elements: Epcot’s World Showcase provides in-depth information about different cultures, absorbing guests in learning experiences.
Encouraging Active Participation:
- Interactive queues: Many ride queues feature games or interactive elements to engage guests while they wait.
- Character meet-and-greets: Visitors can interact directly with Disney characters, often engaging in conversation or activities.
- Participatory shows: Attractions like Turtle Talk with Crush allow audience members to ask questions and influence the show’s direction.
Moving Beyond Memorable to Meaningful:
- Disney Institute: This professional development program offers transformational experiences for businesses and individuals, aligning with participants’ values of personal and professional growth.
- RunDisney events: These running experiences combine fitness goals with Disney magic, creating opportunities for personal achievement and transformation.
Designing for Transformation:
- Understanding customer journeys: Disney uses MagicBands and a robust app to track guest preferences and behaviors, allowing for personalized experiences throughout the park.
- Facilitating personal growth: Disney’s Youth Education Series offers educational programs that blend entertainment with personal development for students.
Measuring Transformation Outcomes:
- Disney Dreamers Academy: This mentorship program for high school students includes follow-ups and alumni events to track long-term impacts on participants’ lives and careers.
Key Characteristics of Transformational Experiences:
- Intensely personal: Disney’s VIP tours offer highly customized experiences tailored to individual preferences and goals.
- Long-term engagement: Disney Vacation Club and Annual Passholder programs foster ongoing relationships and repeated transformative experiences.
Airbnb Experiences
Airbnb has expanded beyond accommodation to offer unique, locally-hosted experiences:
- Entertainment: Concerts in intimate venues, storytelling sessions
- Educational: Cooking classes, artisan workshops
- Esthetic: Photowalks, architecture tours
- Escapist: Adventure sports, cultural immersion experiences
Enhancing Immersion:
- Local hosts: Experiences are led by locals, providing authentic immersion into the destination’s culture.
- Small group sizes: Most experiences are limited to small groups, allowing for a more intimate and immersive environment.
- Unique locations: Many experiences take place in off-the-beaten-path locations, fully immersing participants in local life.
Enhancing Absorption:
- Hands-on activities: Experiences often involve learning new skills, which requires focused attention and absorption.
- Storytelling: Hosts often share personal stories and local histories, capturing participants’ attention.
- Sensory engagement: Many experiences, like food tours or artisan workshops, engage multiple senses to enhance absorption.
Encouraging Active Participation:
- Skill-building workshops: Many experiences involve active learning, such as cooking classes or dance lessons.
- Cultural rituals: Participants often take part in local customs or traditions, actively engaging with the culture.
- Collaborative projects: Some experiences involve group activities or creating something together, fostering active participation.
Moving Beyond Memorable to Meaningful:
- Social Impact Experiences: These experiences connect travelers with local non-profits, aligning with values of social responsibility and personal growth through giving back.
- Airbnb Adventures: Multi-day experiences that offer more profound, potentially life-changing journeys.
Designing for Transformation:
- Understanding customer journeys: Airbnb uses data analytics to recommend experiences based on users’ past bookings and preferences, creating a personalized transformation journey.
- Facilitating personal growth: Many experiences, like language immersion or artistic workshops, are designed to develop new skills and foster personal growth.
Measuring Transformation Outcomes:
- Host and guest reviews: These provide qualitative data on the transformative impact of experiences.
- Skill certification: Some experiences offer certificates of completion, providing tangible proof of new skills acquired.
Key Characteristics of Transformational Experiences:
- Requires active and interested consumers: Experiences often involve hands-on participation and learning, demanding high engagement from participants.
- Clear outcomes: Many experiences have specific learning objectives or skill development goals.
Role of Self-Actualization:
- Both Disney and Airbnb are tapping into higher-level needs on Maslow’s hierarchy. Disney’s immersive environments and character interactions can foster creativity and spontaneity, while Airbnb’s cultural exchanges and skill-building experiences can lead to personal growth and the fulfillment of individual potential.
Creating Meaningful and Transformational Experiences:
- Both companies foster connections: Disney through its community of fans and cast members, and Airbnb through connections between hosts and guests.
- Both emphasize purpose: Disney often frames experiences within larger narratives of heroism or personal growth, while Airbnb emphasizes cultural understanding and personal development.
Media Attributions
- 17-1
- 17-2
- 17-3
- 17-5
