4.3 Intercultural Communication
Learning Objectives
- Define intercultural communication.
- List and summarize the six dialectics of intercultural communication.
It is through intercultural communication that we come to create, understand, and transform culture and identity. Intercultural communication is communication between people with differing cultural identities. One reason we should study intercultural communication is to foster greater self-awareness (Martin & Nakayama, 2010). Our thought process regarding culture is often “other focused,” meaning that the culture of the other person or group is what stands out in our perception. However, the old adage “know thyself” is appropriate, as we become more aware of our own culture by better understanding other cultures and perspectives. Intercultural communication can allow us to step outside of our comfortable, usual frame of reference and see our culture through a different lens. Additionally, as we become more self-aware, we may also become more ethical communicators as we challenge our ethnocentrism, or our tendency to view our own culture as superior to other cultures.
As was noted earlier, difference matters, and studying intercultural communication can help us better negotiate our changing world. Changing economies and technologies intersect with culture in meaningful ways (Martin & Nakayama). As was noted earlier, technology has created for some a global village where vast distances are now much shorter due to new technology that make travel and communication more accessible and convenient (McLuhan, 1967). However, as the following “Getting Plugged In” box indicates, there is also a digital divide, which refers to the unequal access to technology and related skills that exists in much of the world. People in most fields will be more successful if they are prepared to work in a globalized world. Obviously, the global market sets up the need to have intercultural competence for employees who travel between locations of a multinational corporation. Perhaps less obvious may be the need for teachers to work with students who do not speak English as their first language and for police officers, lawyers, managers, and medical personnel to be able to work with people who have various cultural identities.
Intercultural Communication: A Dialectical Approach
Intercultural communication is complicated, messy, and at times contradictory. Therefore it is not always easy to conceptualize or study. Taking a dialectical approach allows us to capture the dynamism of intercultural communication. A dialectic is a relationship between two opposing concepts that constantly push and pull one another (Martin & Nakayama, 2010). To put it another way, thinking dialectically helps us realize that our experiences often occur in between two different phenomena. This perspective is especially useful for interpersonal and intercultural communication, because when we think dialectically, we think relationally. This means we look at the relationship between aspects of intercultural communication rather than viewing them in isolation. Intercultural communication occurs as a dynamic in-betweenness that, while connected to the individuals in an encounter, goes beyond the individuals, creating something unique. Holding a dialectical perspective may be challenging for some Westerners, as it asks us to hold two contradictory ideas simultaneously, which goes against much of what we are taught in our formal education. Thinking dialectically helps us see the complexity in culture and identity because it doesn’t allow for dichotomies. Dichotomies are dualistic ways of thinking that highlight opposites, reducing the ability to see gradations that exist in between concepts. Dichotomies such as good/evil, wrong/right, objective/subjective, male/female, in-group/out-group, black/white, and so on form the basis of much of our thoughts on ethics, culture, and general philosophy, but this isn’t the only way of thinking (Marin & Nakayama, 1999). Many Eastern cultures acknowledge that the world isn’t dualistic. Rather, they accept as part of their reality that things that seem opposite are actually interdependent and complement each other. I argue that a dialectical approach is useful in studying intercultural communication because it gets us out of our comfortable and familiar ways of thinking. Since so much of understanding culture and identity is understanding ourselves, having an unfamiliar lens through which to view culture can offer us insights that our familiar lenses will not. Specifically, we can better understand intercultural communication by examining six dialectics (see Figure 4.3.1 “Dialectics of Intercultural Communication”) (Martin & Nakayama, 1999).
Figure 4.3.1: Dialectics of Intercultural Communication
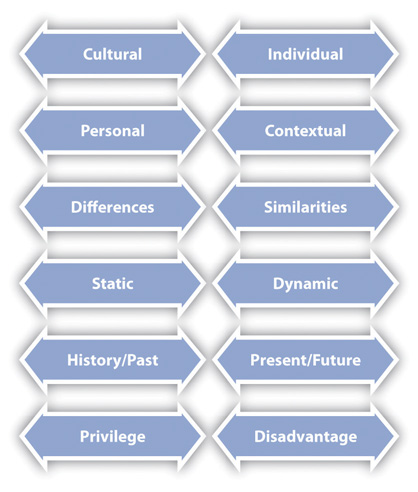
The cultural-individual dialectic captures the interplay between patterned behaviors learned from a cultural group and individual behaviors that may be variations on or counter to those of the larger culture. This dialectic is useful because it helps us account for exceptions to cultural norms. For example, earlier we learned that the United States is said to be a low-context culture, which means that we value verbal communication as our primary, meaning-rich form of communication. Conversely, Japan is said to be a high-context culture, which means they often look for nonverbal clues like tone, silence, or what is not said for meaning. However, you can find people in the United States who intentionally put much meaning into how they say things, perhaps because they are not as comfortable speaking directly what’s on their mind. We often do this in situations where we may hurt someone’s feelings or damage a relationship. Does that mean we come from a high-context culture? Does the Japanese man who speaks more than is socially acceptable come from a low-context culture? The answer to both questions is no. Neither the behaviors of a small percentage of individuals nor occasional situational choices constitute a cultural pattern.
The personal-contextual dialectic highlights the connection between our personal patterns of and preferences for communicating and how various contexts influence the personal. In some cases, our communication patterns and preferences will stay the same across many contexts. In other cases, a context shift may lead us to alter our communication and adapt. For example, an American businesswoman may prefer to communicate with her employees in an informal and laid-back manner. When she is promoted to manage a department in her company’s office in Malaysia, she may again prefer to communicate with her new Malaysian employees the same way she did with those in the United States. In the United States, we know that there are some accepted norms that communication in work contexts is more formal than in personal contexts. However, we also know that individual managers often adapt these expectations to suit their own personal tastes. This type of managerial discretion would likely not go over as well in Malaysia where there is a greater emphasis put on power distance (Hofstede, 1991). So while the American manager may not know to adapt to the new context unless she has a high degree of intercultural communication competence, Malaysian managers would realize that this is an instance where the context likely influences communication more than personal preferences.
The differences-similarities dialectic allows us to examine how we are simultaneously similar to and different from others. As was noted earlier, it’s easy to fall into a view of intercultural communication as “other oriented” and set up dichotomies between “us” and “them.” When we overfocus on differences, we can end up polarizing groups that actually have things in common. When we over-focus on similarities, we essentialize, or reduce/overlook important variations within a group. This tendency is evident in most of the popular, and some of the academic, conversations regarding “gender differences.” The book Men Are from Mars and Women Are from Venus makes it seem like men and women aren’t even species that hail from the same planet. The media is quick to include a blurb from a research study indicating again how men and women are “wired” to communicate differently. However, the overwhelming majority of current research on gender and communication finds that while there are differences between how men and women communicate, there are far more similarities (Allen, 2011). Even the language we use to describe the genders sets up dichotomies. That’s why I suggest that my students use the term other gender instead of the commonly used opposite sex. I have a mom, a sister, and plenty of female friends, and I don’t feel like any of them are the opposite of me. Perhaps a better title for a book would be Women and Men Are Both from Earth.
The static-dynamic dialectic suggests that culture and communication change over time yet often appear to be and are experienced as stable. Although it is true that our cultural beliefs and practices are rooted in the past, we have already discussed how cultural categories that most of us assume to be stable, like race and gender, have changed dramatically in just the past fifty years. Some cultural values remain relatively consistent over time, which allows us to make some generalizations about a culture. For example, cultures have different orientations to time. The Chinese have a longer-term orientation to time than do Europeans (Lustig & Koester, 2006). This is evidenced in something that dates back as far as astrology. The Chinese zodiac is done annually (The Year of the Monkey, etc.), while European astrology was organized by month (Taurus, etc.). While this cultural orientation to time has been around for generations, as China becomes more Westernized in terms of technology, business, and commerce, it could also adopt some views on time that are more short term.
The history/past-present/future dialectic reminds us to understand that while current cultural conditions are important and that our actions now will inevitably affect our future, those conditions are not without a history. We always view history through the lens of the present. Perhaps no example is more entrenched in our past and avoided in our present as the history of slavery in the United States. Where I grew up in the Southern United States, race was something that came up frequently. The high school I attended was 30 percent minorities (mostly African American) and also had a noticeable number of white teens (mostly male) who proudly displayed Confederate flags on their clothing or vehicles.
I remember an instance in a history class where we were discussing slavery and the subject of repatriation, or compensation for descendants of slaves, came up. A white male student in the class proclaimed, “I’ve never owned slaves. Why should I have to care about this now?” While his statement about not owning slaves is valid, it doesn’t acknowledge that effects of slavery still linger today and that the repercussions of such a long and unjust period of our history don’t disappear over the course of a few generations.
The privileges-disadvantages dialectic captures the complex interrelation of unearned, systemic advantages and disadvantages that operate among our various identities. As was discussed earlier, our society consists of dominant and nondominant groups. Our cultures and identities have certain privileges and/or disadvantages. To understand this dialectic, we must view culture and identity through a lens of intersectionality, which asks us to acknowledge that we each have multiple cultures and identities that intersect with each other. Because our identities are complex, no one is completely privileged and no one is completely disadvantaged. For example, while we may think of a white, heterosexual male as being very privileged, he may also have a disability that leaves him without the able-bodied privilege that a Latina woman has. This is often a difficult dialectic for my students to understand, because they are quick to point out exceptions that they think challenge this notion. For example, many people like to point out Oprah Winfrey as a powerful African American woman. While she is definitely now quite privileged despite her disadvantaged identities, her trajectory isn’t the norm. When we view privilege and disadvantage at the cultural level, we cannot let individual exceptions distract from the systemic and institutionalized ways in which some people in our society are disadvantaged while others are privileged.
As these dialectics reiterate, culture and communication are complex systems that intersect with and diverge from many contexts. A better understanding of all these dialectics helps us be more critical thinkers and competent communicators in a changing world.
“Getting Critical”
Immigration, Laws, and Religion
France, like the United States, has a constitutional separation between church and state. As many countries in Europe, including France, Belgium, Germany, the Netherlands, and Sweden, have experienced influxes of immigrants, many of them Muslim, there have been growing tensions among immigration, laws, and religion. In 2011, France passed a law banning the wearing of a niqab (pronounced knee-cobb), which is an Islamic facial covering worn by some women that only exposes the eyes. This law was aimed at “assimilating its Muslim population” of more than five million people and “defending French values and women’s rights” (De La Baume & Goodman, 2011). Women found wearing the veil can now be cited and fined $150 euros. Although the law went into effect in April of 2011, the first fines were issued in late September of 2011. Hind Ahmas, a woman who was fined, says she welcomes the punishment because she wants to challenge the law in the European Court of Human Rights. She also stated that she respects French laws but cannot abide by this one. Her choice to wear the veil has been met with more than a fine. She recounts how she has been denied access to banks and other public buildings and was verbally harassed by a woman on the street and then punched in the face by the woman’s husband. Another Muslim woman named Kenza Drider, who can be seen in Video Clip 8.2, announced that she will run for the presidency of France in order to challenge the law. The bill that contained the law was broadly supported by politicians and the public in France, and similar laws are already in place in Belgium and are being proposed in Italy, Austria, the Netherlands, and Switzerland (Fraser, 2011).
- Some people who support the law argue that part of integrating into Western society is showing your face. Do you agree or disagree? Why?
- Part of the argument for the law is to aid in the assimilation of Muslim immigrants into French society. What are some positives and negatives of this type of assimilation?
- Identify which of the previously discussed dialectics can be seen in this case. How do these dialectics capture the tensions involved?
Video Clip 4.3.1
Veiled Woman Eyes French Presidency
Cultural Value Dimensions
The ways in which we communicate reflect and sustain cultural values. In his research, Geert Hofstede (1999; 2012; Bhawuk, 2017)) identified various cultural dimensions that differentiate values across cultures. These values influence communication and behaviors among different societies: power distance, individualism and collectivism, high and low context message orientation, femininity and masculinity, uncertainty avoidance, and long and short term orientation.
Power Distance
Power distance “concerns the extent to which those with authority (at the top) are similar to or very different from those at the bottom of a social structure” (Bhawuk, p. 9). All societies are unequal to some extent, but some are more unequal than others. High power distance cultures emphasize maintaining the inequalities among those in authority and those with less power. Low power distance cultures place value on challenging authority, redistributing ownership, and flattening hierarchies. For example, “in a high power distance culture like Hong Kong, a superior could insult a subordinate with impunity, but such behavior might not be acceptable in a lower power distance culture like Denmark” (p. 9). The United States leans toward low power distance.
Table 4.3.1 Power Distance
| Power Distance: the degree to which the less powerful members of societies accept and expect that power is distributed unequally | ||
| Behaviors & Characteristics | Country Examples | |
| High power distance | Power is a basic fact of society, hierarchies are accepted, those in authority are right and are seldom questioned, parents teach children obedience, subordinates expect to be told what to do, older people are respected and feared, corruption is common and scandals are covered up, rank has privileges | Venezuela, Mexico, the Philippines, Yugoslavia, Middle Eastern countries |
| Low power distance | Power should be legitimate, parents treat children as equals, subordinates expect to be consulted, older people are neither feared or respected, corruption is rare and scandals are made public, subordinates must come to work on time, relatively rich populations | Denmark, Austria, Israel, Sweden, |
Individualism/Collectivism
Individualism and collectivism concern the degree to which people in a society are integrated into groups. People in individualistic countries prefer to act as individuals rather than as members of group. In contrast, people in collectivistic countries value their group experience and identify with the groups to which they belong (p. 46). Keep in mind that there can be aspects of collectivism and individualism present in any society, yet the overarching philosophy of a country is usually steeped in one or the other.
Table 4.3.2 Individualism/Collectivism
| Collectivism/Individualism: The degree to which members of a society are integrated into groups | ||
| Behaviors & Characteristics | Country Examples | |
| Collectivism | Focus on belonging, “we” orientation, harmony is maintained, others are classified as in-groups and out-groups, decisions & opinions are made by the in-group, relationships are more important than the task, self-concept depends on group success | Mexico, Columbia, China, Pakistan, Costa Rica, Japan, India, Russia |
| Individualism | Focus on the individual, privacy is important, speaking your mind is healthy, others are classified as individuals, personal opinion is expected, one person-one vote, task is more important than relationships, self-concept depends on individual success | United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Denmark, Sweden, New Zealand, Italy, |
High/Low-Context
High and low context message orientation concerns the importance of contextual cues in interpreting a message. In a high context culture, contextual cues are message-laden. Communication is based on body language, tone, and overall context – not in the words that are used. In contrast, low context cultures rely on verbal communication to communicate a message. Communication is straightforward and direct. If you were from a high context culture, you would think that a person from a low context culture was blunt, too forward, and possibly rude. Yet, a person from a low context culture would wonder why you never said what you meant, and why you always “beat around the bush”.
Table 4.3.3 High/Low-Context
|
High and Low Context Message Orientation: the degree to which contextual cues are important in interpreting a message |
||
| Behaviors & Characteristics | Country Examples | |
| High Context | Nonverbal communication communicates the message, meaning is in what is NOT said,
Relies less on words or verbal communication to convey meaning, receivers have to read between the lines for meaning |
Asian cultures, Middle Eastern cultures, African cultures |
| Low Context | Words in the interaction communicate meaning, say what you mean & mean what you say, tell it like it is, reliance on verbal communication, directness, receivers take message meaning at face value | Switzerland, Germany, United States, Scandinavia, |
Feminine/Masculine
Femininity & Masculinity concern the degree to which behaviors generally associated with men or women are valued in a society. Feminine behaviors include tender values like quality of life, maintaining relationships, service, and care for the weak. Masculine cultures prefer tough values like assertiveness, performance, success, and competition. The United States is more masculine than feminine. It important to note that the level of femininity or masculinity doesn’t mean that a culture treats women as well as men. It means that gender roles in feminine cultures are more fluid than in masculine cultures.
Table 4.3.4 Feminine/Masculine
|
Femininity & Masculinity: the degree to which behaviors generally associated with men or women are valued in a society |
||
| Behaviors | Country Examples | |
| Femininity | Fluid & overlapping gender roles, nurturance, support, achievement defined by lifestyle, “work to live,” balance between family & work, sympathy for the weak, both fathers and mothers deal with facts and feelings, both boys & girls may cry, but neither should fight, many women in elected political positions, mothers decide numbers of children | Sweden, Norway, the Netherlands, Denmark, Yugoslavia |
| Masculinity | rigid, clearly distinct gender roles, achievement defined by wealth, “live to work,” admiration for the strong, fathers deal with facts — mothers with feelings, girls cry – boys don’t, boys fight back – girls don’t, few women in elected political positions, fathers decide on family size | Japan, Austria, Venezuela, Italy, Switzerland |
Uncertainty Avoidance
Uncertainty avoidance “refers to the creation of rules and bureaucracy to avoid ambiguity in behavior” (p. 9). Simply put, to what degree do the people in a society prefer structured over unstructured situations? A high uncertainty avoidance society needs structure. Rules are needed even if they’re not obeyed. In contrast, a low uncertainty avoidance culture dislikes rules, written or unwritten.
Table 4.3.5 Uncertainty Avoidance
|
Uncertainty Avoidance: the degree of tolerance for ambiguity in a society |
||
| Behaviors & Characteristics | Country Examples | |
| High Uncertainty Avoidance | Uncertainty is a threat, higher stress, emotionality, anxiety, lower scores on health and well-being, conformity, avoid situations with uncertain outcomes, teachers have all the answers, need for clarity and structure | Japan, Greece, Russia, Poland, Belgium, Italy, Korea, Portugal, Uruguay |
| Low Uncertainty Avoidance | Uncertainty is accepted, easy-going, lower stress, self-control, low anxiety, higher scores on health & well-being, teachers can may say, “I don’t know,” comfortable with ambiguity and chaos | Hong Kong, Canada, Singapore, Jamaica, Scandinavia, United States, China, India, United Kingdom, |
Long/Short-term Orientation
Long and short term orientation concerns the extent to which a society looks forward to the future rather than resorting to the past to solve problems in the present or the future. “Long term orientation stands for the fostering of virtues oriented towards future rewards, in particular, perseverance and thrift. Its opposite pole, short term orientation, stands for the fostering of virtues related to the past and present, in particular, respect for tradition, preservation of ‘face’ and fulfilling social obligations” (Hofstede, 2010, p. 359).
Table 4.3.6 Long/Short-Term Orientation
|
Short & Long Term Orientation: the extent to which a society looks forward to the future rather than resorting to the past to solve problem in the present or the future |
||
| Behaviors & Characteristics | Country Examples | |
| Long term orientation | Emphasis on persistence, personal adaptability important, leisure time not too important, relationships important, focused on the future, value savings and investments, value perseverance, tenacity & thrift, dynamic mindset toward the future, long term relationships are valuable, respect traditions – but prepare for the future, flexible toward change, focus on long term goals, changes are made easily | China, India, Russia, Japan, Sweden, Norway, Finland, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, Argentina, Chile |
| Short term orientation | Emphasis on quick results, personal steadfastness important, leisure time important, bottom line important, focused on immediate needs, value social spending & consumption, prefer quick results, look to the past to solve problems, stability is valued, maintain conventional behaviors, maintain a fixed mindset, make short-term goals, resist change, allow less room for progress (Ehsanfar, 2019) | Morroco, Algeria, Libya, Saudi Arabia, Iran, |
Key Takeaways
- Studying intercultural communication, communication between people with differing cultural identities, can help us gain more self-awareness and be better able to communicate in a world with changing demographics and technologies.
- A dialectical approach to studying intercultural communication is useful because it allows us to think about culture and identity in complex ways, avoiding dichotomies and acknowledging the tensions that must be negotiated.
Exercises
- Why is the phrase “Know thyself” relevant to the study of intercultural communication?
- Apply at least one of the six dialectics to a recent intercultural interaction that you had. How does this dialectic help you understand or analyze the situation?
References
Allen, B. J., Difference Matters: Communicating Social Identity, 2nd ed. (Long Grove, IL: Waveland, 2011), 55.
ben-Aaron, D., “Bringing Broadband to Finland’s Bookdocks,” Bloomberg Businessweek, July 19, 2010, 42.
Bhawuk, D. P. S. (2017). Cultural value dimensions, in Kim, Y. Y., (Ed). The International Encyclopedia of Intercultural Communication, John Wiley & sons, https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118783665.ieicc0101.
Chen, Y. and Masato Nakazawa, “Influences of Culture on Self-Disclosure as Relationally Situated in Intercultural and Interracial Friendships from a Social Penetration Perspective,” Journal of Intercultural Communication Research 38, no. 2 (2009): 94. doi:10.1080/17475750903395408.
Coller, M. J., “Communication Competence Problematics in Ethnic Friendships,” Communication Monographs 63, no. 4 (1996): 324–25.
De La Baume, M. and J. David Goodman, “First Fines over Wearing Veils in France,” The New York Times (The Lede: Blogging the News), September 22, 2011, accessed October 10, 2011, http://thelede.blogs.nytimes.com/2011/09/22/first-fines-over -wearing-full-veils-in-france.
Ehsanfar, E. (2019). Hofstede’s long term orientation. https://www.rubeana.com/2019/07/15/hofstedes-long-term-orientation/ . Accessed July 21,
2023.
Fraser, C., “The Women Defying France’s Fall-Face Veil Ban,” BBC News, September 22, 2011, accessed October 10, 2011, http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-15023308.
Gaines Jr. S. O., and Kelly A. Brennan, “Establishing and Maintaining Satisfaction in Multicultural Relationships,” in Close Romantic Relationships: Maintenance and Enhancement, eds. John Harvey and Amy Wenzel (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum, 2011), 239.
Hofstede, G. (1999). Cultural constraints in management theories. Perspectives: Intercultural Communication. G. Perry (Ed.). Chicago, IL: Coursewise Publishing.
Hofstede, G., Hofstede, G. J., Minkov, M. (2010). Cultures and Organizations: Software of the Mind, 3rd Ed. USA: McGraw-Hill.
Hofstede, G. (2012). Dimensionalizing cultures: The Hofstede model in context. In S. J. Kulich, M. H. Prosser, & L. P. Weng (Eds.). Value frameworks at the theoretical crossroads of culture,
pp. 183–215. Shanghai, China: Shanghai Foreign Language Education Press.
Stanley O. Gaines Jr., S. O., and James H. Liu, “Multicultural/Multiracial Relationships,” in Close Relationships: A Sourcebook, eds. Clyde Hendrick and Susan S. Hendrick (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000), 105.
Hofstede, G., Cultures and Organizations: Softwares of the Mind (London: McGraw-Hill, 1991), 26.
Human Rights Campaign, “Pass ENDA NOW”, accessed November 5, 2012, http://www.hrc.org/campaigns/employment-non-discrimination-act.
Lee, P., “Bridging Cultures: Understanding the Construction of Relational Identity in Intercultural Friendships,” Journal of Intercultural Communication Research 35, no. 1 (2006): 11. doi:10.1080/17475740600739156.
Loving Day, “The Last Laws to Go,” Lovingday.org, accessed October 11, 2011, http://lovingday.org/last-laws-to-go.
Lustig, M. W., and Jolene Koester, Intercultural Competence: Interpersonal Communication across Cultures, 2nd ed. (Boston, MA: Pearson, 2006), 128–29.
Martin, J. N., and Thomas K. Nakayama, Intercultural Communication in Contexts, 5th ed. (Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill, 2010), 4.
Martin, J. N., and Thomas K. Nakayama, “Thinking Dialectically about Culture and Communication,” Communication Theory 9, no. 1 (1999): 14.
McLuhan, M., The Medium Is the Message (New York: Bantam Books, 1967).
Peplau, L. A. and Leah R. Spalding, “The Close Relationships of Lesbians, Gay Men, and Bisexuals,” in Close Relationships: A Sourcebook, eds. Clyde Hendrick and Susan S. Hendrick (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000), 113.
Pratt, R. A., “Crossing the Color Line: A Historical Assessment and Personal Narrative of Loving v. Virginia,” Howard Law Journal 41, no. 2 (1995): 229–36.
Sias, P. M., Jolanta A. Drzewiecka, Mary Meares, Rhiannon Bent, Yoko Konomi, Maria Ortega, and Colene White, “Intercultural Friendship Development,” Communication Reports 21, no. 1 (2008): 9. doi:10.1080/08934210701643750.
Smith, P., “The Digital Divide,” New York Times Upfront, May 9, 2011, 6.
Sylvester, D. E., and Adam J. McGlynn, “The Digital Divide, Political Participation, and Place,” Social Science Computer Review 28, no. 1 (2010): 64–65. doi:10.1177/0894439309335148.
van Deursen, A. and Jan van Dijk, “Internet Skills and the Digital Divide,” New Media and Society 13, no. 6 (2010): 893. doi:10.1177/1461444810386774.
Communication between people with differing cultural identities
The tendency to view your own culture as superior to other cultures
All parts of the world being brought together due to technologies that make travel and communication more accessible and convenient
The unequal access to technology and related skills that exists in much of the world
A relationship between two opposing concepts that constantly push and pull one another
Dualistic ways of thinking that highlight opposites, reducing the ability to see gradations that exist in between concepts; for example, good/evil, right/wrong, male/female, etc.
Refers to the interplay between patterned behaviors learned from a cultural group and individual behaviors that may be variations on or counter to those of the larger culture
The connection between our personal patterns of and preferences for communicating and how various contexts influence the personal
A dialectic that focuses on how we are simultaneously similar to and different from others
To over-focus on similarities or reduce/overlook important variations within a group
A dialectic that suggest culture and communication change over time yet often appear to be and are experienced as stable
A dialectic that reminds us to understand that while current cultural conditions are important and that our actions will inevitably affect our future, those conditions are nor without a history; holds that we always view history through the lens of the present
A dialectic that captures the complex interrelation of unearned, systemic advantages and disadvantages that operate among our various identities
A view which asks us to acknowledge that we each have multiple cultures and identities that intersect with each other

