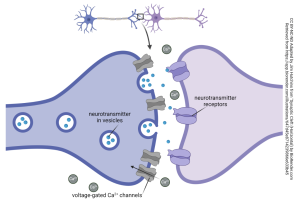
Neurotransmitters: Serotonin
Mia Verbeck and Jim Hutchins
Chapter under construction. This is the first draft. If you have questions, or want to help in the writing or editing process, please contact hutchins.jim@gmail.com.
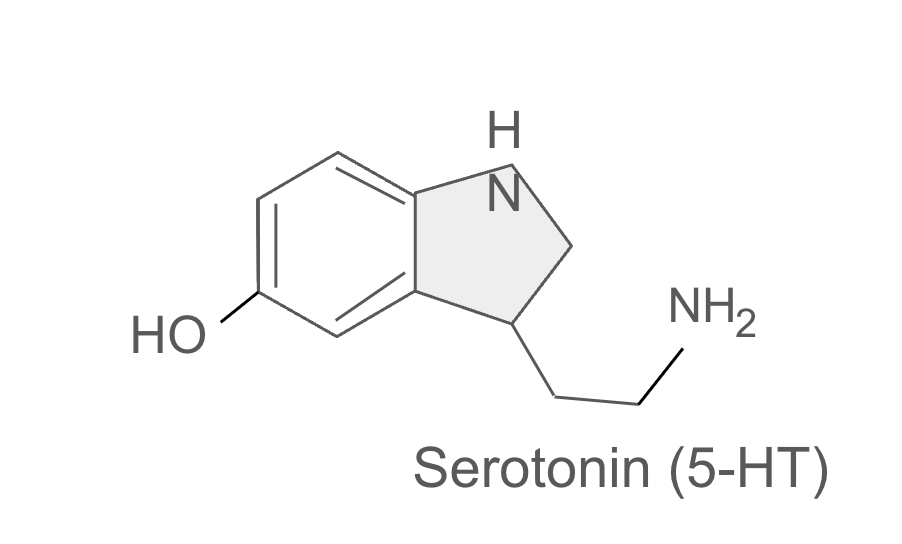
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter. It can be found throughout the body mainly within our brain and intestines. It is a biogenic amine that is derived from tryptophan through a process called serotonin biosynthesis. Serotonin is known for regulating mood, controlling appetite, promoting sleep, and aiding in digestion. It is a very important transmitter to maintain our well-being.
Serotonin Biosynthesis
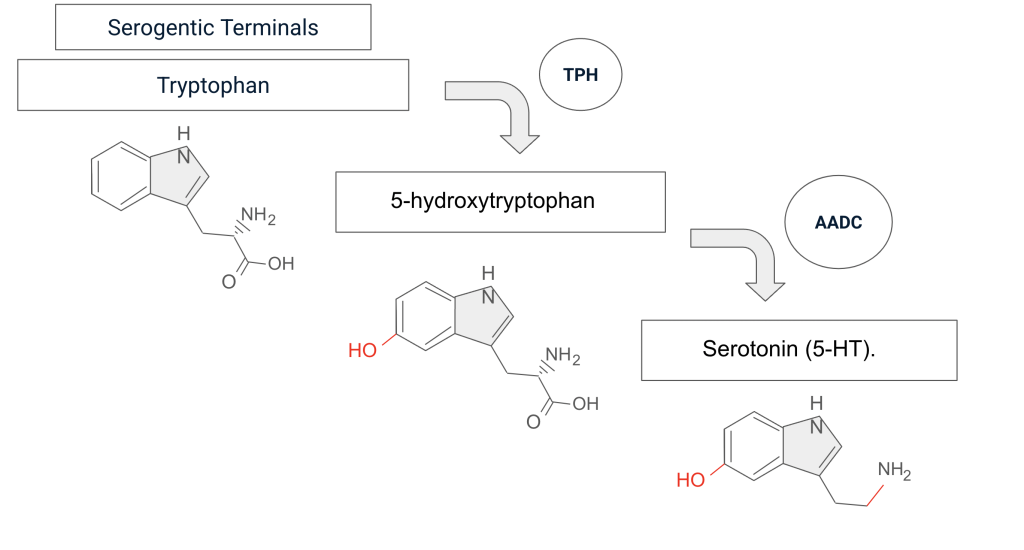
The first step to serotonin biosynthesis involves an amino acid called tryptophan. We obtain tryptophan through our diet in food such as eggs, turkey, cheese and nuts. Once these food are broken down the amino acid is taken up by neurons and other cells to be synthesized. In our brain it is taken up by serotonergic neurons while in our gastrointestinal tract, which holds 90-95% of our serotonin, it is synthesized by enteric neurons.
The second step happens within the serotonergic terminals within those neurons. This step involves the hydroxylation of tryptophan catalyzed by the enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase (THP). This enzyme requires tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) in order to function properly. There are two isoforms of tryptophan hydroxylase:
- TPH1 : Found in peripheral tissue, such as the gut.
- TPH2 : Found in mainly in the brain.
This process transforms tryptophan in to 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP).
The last step is decarboxylation of 5-HTP. This is process is catalyzed by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AAAD), which is commonly know as dopamine decarboxylase. This transforms 5-HTP in serotonin (5-HT). This step does not require the presence of a cofactor beside pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6) to function properly.
Storage and Metabolism
Serotonin is stored within vesicles in Serotonergic neurons. To package serotonin into vesicles it uses a proton pump, reducing pH inside the vesicle and creating a higher concentration of protons compared to the cytoplasm outside the vesicle The proton then drives an vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) which uses a proton gradient to move the serotonin into the vesicle which uses ATP for energy. It is released in response to neural activity.
Serotonin is metabolized by monoamine oxidase (MOA). When it breaks down serotonin it transforms the neurotransmitter into 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) which is then excreted through urine.
Reuptake
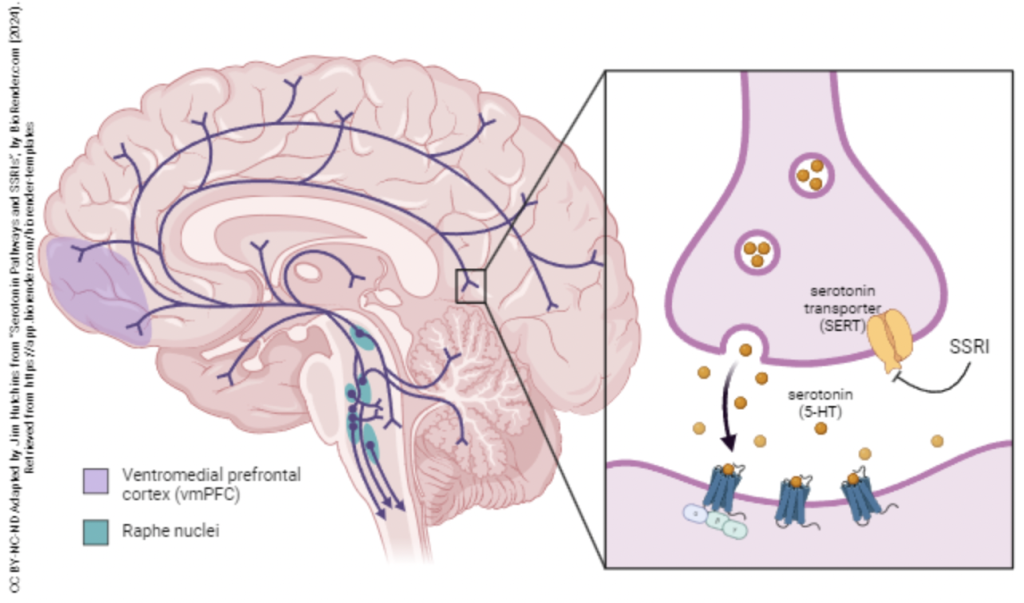
Reuptake of serotonin is done by the serotonin transporter (SERT) which is located on the presynaptic membrane of the neuron. When serotonin is left in the synaptic cleft, it will transport it back to the presynaptic neuron to be used for future signaling. This process requires sodium ions (Na+) due to it being a sodium-dependent cotransport system. Once this process happens it has two options:
- Repackaged into a synaptic vesicle: This is where it can be used for future signaling
- Metabolized: Broken down by a MOA to be extracted through urine.
Reuptake contribute a huge part in regulating serotonin levels. However certain drugs such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can block the reuptake mechanisms, this increasing the availability of serotonin which is why SSRIs are commonly as antidepressant.
Serotonin Receptors
Serotonin receptors are grouped G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and ligand ion channels. These mediate the effects of serotonin on the cell. There are at least 7 major families of serotonin receptors. They range from 5-HT1 – 5-HT7 each with subtypes besides 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 the function of each receptors are:
- 5-HT1: Inhibitory, involved with mood regulation and anxiety. (Located in the brain; Hippocampus and cortex).
- 5-HT2: Excitatory, involved with vascular tone, psychosis, and mood. (Located in the brain; Limbic system, cortex and certain blood vessels).
- 5-HT3: Ion Channels, involved with nausea and vomiting. (Located in the central and peripheral nervous system as well as the gastrointestinal tract).
- 5-HT4: Excitatory, involved with gastrointestinal motility. (Located in the gastrointestinal tract in the stomach and intestines it is also in the brain).
- 5-HT5: NA, involved with neurotransmission. (Located in the brain; hippocampus).
- 5-HT6: Excitatory, involved with cognition, mood, and neurodegenerative diseases. (Located in the brain; striatum and cortex).
- 5-HT7: Excitatory, involved with circadian rhythms and sleep. (Located in the brain, blood vessels and gastrointestinal tract).
Roles of Serotonin
Psychological
Serotonin plays a huge role in our mental and psychical well being. It influence many parts of the brain that control mood regulation, cognitive function such as leaning and memory, neurodevelopment, and sleep-wake cycle. These are all very vital functions our body needs in order to survive.
Peripheral System
Serotonin also helps a lot with our bodily functions. It works within our;
- immune system, It effect the production of cytokines which are involved with inflammation.
- vascular system, It effects our heart rate and blood pressure, if our levels are too high it will. cause hypertension.
- gastrointestinal system, It regulates appetite, effect bowl movements for example it we have lower levels of serotonin it can contribute to constipation vice versa.
Disorders
Serotonin plays a huge role in many disorders either that being the presences of serotonin or the lack of it.
- Depression, is a commonly know disorder cause by the lower levels of serotonin.
- Anxiety Disorders, a dysregulation of serotonin levels which can lead to generalized anxiety or panic attacks.
- Schizophrenia, serotonin modulated dopamine pathways in schizophrenia.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), Serotonergic dysfunction role.
- Serotonin syndrome, to much serotonin causing neuromuscular abnormalities and sudden death.
Media Attributions
- Screen Shot 2025-02-22 at 8.13.33 PM
- Screen Shot 2025-02-22 at 8.17.30 PM
- Screen Shot 2025-02-03 at 1.43.40 PM © Cierra Memphis Barnett is licensed under a CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution NonCommercial NoDerivatives) license
- Canonical synapse © BioRender adapted by Jim Hutchins is licensed under a CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution NonCommercial NoDerivatives) license
- Serotonin Pathways and SSRIs © BioRender adapted by Jim Hutchins is licensed under a CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution NonCommercial NoDerivatives) license
organic compound of amine groups. This are created when amino acids are decarboxylated during fermentation.
Addition of -OH to a chemical structure.
The removal of a carboxyl group,
(-COOH)