3 The Governance of Education
Questions for Discussion:
- How is education governed?
- Who is ultimately responsible or in charge of education?
- How is education funded (teacher salaries, schools, etc.)?
- What part does the United States Constitution play in determining how education is governed?
- What is the physical plant of a school? What are the necessary parts of a school besides teachers?
- What are some examples of standards established by the Utah State Board of Education? (Strands and Standards, Teaching as a Profession 3 CTE)
Teacher Feature
Secondary Spanish Teacher and Coach Rob Ward, Rob Ward.
Teacher Feature Reflection Questions:
- Why did Mr. Ward become a teacher and coach?
- What does Mr. Ward believe makes him a good teacher?
- What is Mr. Ward’s favorite part of being a teacher?
- What advice would Mr. Ward give to new teachers?
Utah Education Flashback
Martin Slack was one of the first teachers in Toquerville Utah in 1866. He was the first Secretary of Kane County and Secretary of the Hurricane Canal Company. He was elected judge and taught a free night school for adults (Under Dixie Sun: A history of Washington County (1950). Panguitch, UT: Garfield County News.)
The Governance of Education
The governance of education refers to the system of policies, regulations, and decision-making structures that guide the operation of schools and other educational institutions. In the United States, education governance is shared among federal, state, and local governments.
The Federal Government’s Role in Education
At the federal level, the U.S. Department of Education is responsible for developing policies related to education, providing funding to schools and districts, and monitoring compliance with federal laws such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act and the No Child Left Behind Act. The federal government also provides financial aid to students through programs such as Pell Grants and Stafford Loans.
State Government’s Role in Education
At the state level, state departments of education are responsible for implementing and enforcing education policies and regulations. State governments provide most of the funding for public education, and establish standards for student achievement, teacher certification, and school accountability.
The Local (County) Government’s Role in Education
At the local level, school districts or the Local Education Agency (LEA) are responsible for managing individual schools and providing education services to students. School boards are typically responsible for setting policies and overseeing the operation of schools within a district. Local property taxes provide a significant portion of funding for public schools.
In addition to these government entities, other organizations, and stakeholders may also have a role in education governance. For example, parent-teacher associations, community organizations, and teacher unions may advocate for policies and programs that support students and teachers. The National Education Association, American Federation of Teachers, Utah Education Association, and Washington County Education Association are all examples of professional organizations that have active participation in Utah LEAs.
Washington County, Utah, educational governance is primarily the responsibility of the Washington County School District (WCSD) and the Utah State Board of Education (USBE).
The Washington County School District (the LEA) is responsible for managing the K-12 education system within the county, including overseeing the district’s schools, setting policies and procedures, hiring and evaluating staff, and managing the district’s budget. The district is overseen by a seven-member elected school board, each serving a four-year term.
The Utah State Board of Education (USBE)provides oversight and guidance to all school districts within the state, including the Washington County School District. The board is responsible for developing and implementing education policies, setting standards and curricula, and administering state and federal education programs.
The Utah State Office of Education (USOE) provides support and resources to school districts across the state, including the Washington County School District. The USOE is responsible for administering statewide assessments, providing technical assistance to schools and districts, and developing and implementing statewide education initiatives.
In addition to the Washington County School District, several charter schools are operating within the county, which are overseen by the Utah State Charter School Board. These schools operate independently of the traditional public school system and have their own governing boards and policies. These charter schools are still subject to state and federal education regulations and oversight.
County collected property tax contributes the greatest amount of money to Local Education Agencies (LEAs) or school districts. Examine the local tax notice below and see if you can determine how your tax dollars are spend on education.
Who pays for education? Examine the following tax statement.
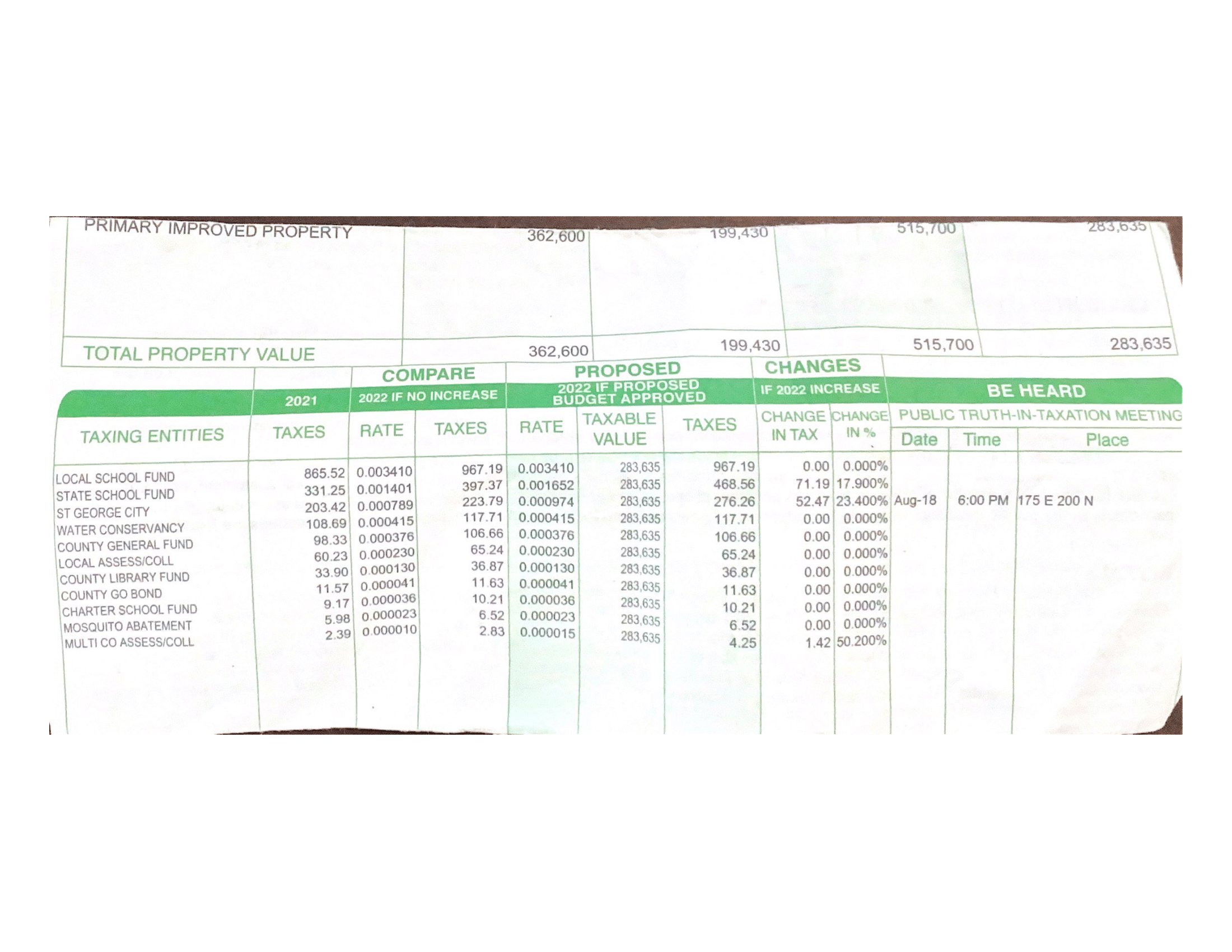
Governing Education in Utah
In Utah, education governance is primarily the responsibility of the Utah State Board of Education, which is composed of 15 elected members who serve four-year terms. The board is responsible for setting statewide education policies, approving academic standards, and allocating funding to school districts and charter schools.
The Utah State Board of Education is also responsible for overseeing the state’s public education system, which includes K-12 schools and technical colleges. In addition, the board sets requirements for teacher certification and oversees the licensing of educators in the state.
Local school districts are responsible for implementing state policies and providing education services to students. There are 41 local school districts in Utah, each of which is governed by an elected school board. School boards are responsible for hiring district personnel, approving budgets, and setting policies that are in line with state and federal education laws.
Charter schools are another important part of Utah’s education system, and are governed by their own boards of directors. Charter schools receive state funding, but are exempt from many of the regulations that apply to traditional public schools.
The Utah State Office of Education provides support to schools and districts across the state, and is responsible for implementing statewide education initiatives and programs. The office provides resources and support to teachers, school administrators, and students, and helps to ensure that schools are meeting state and federal education requirements.
The State of Utah educational system and how it is organized can is best represented through accessing the Utah Education Network (UEN). UEN is a collaborative network of public and higher education institutions in Utah that provides digital resources and support for teaching and learning. UEN offers a variety of online tools and resources for educators and students, including online courses, digital textbooks, and virtual field trips.
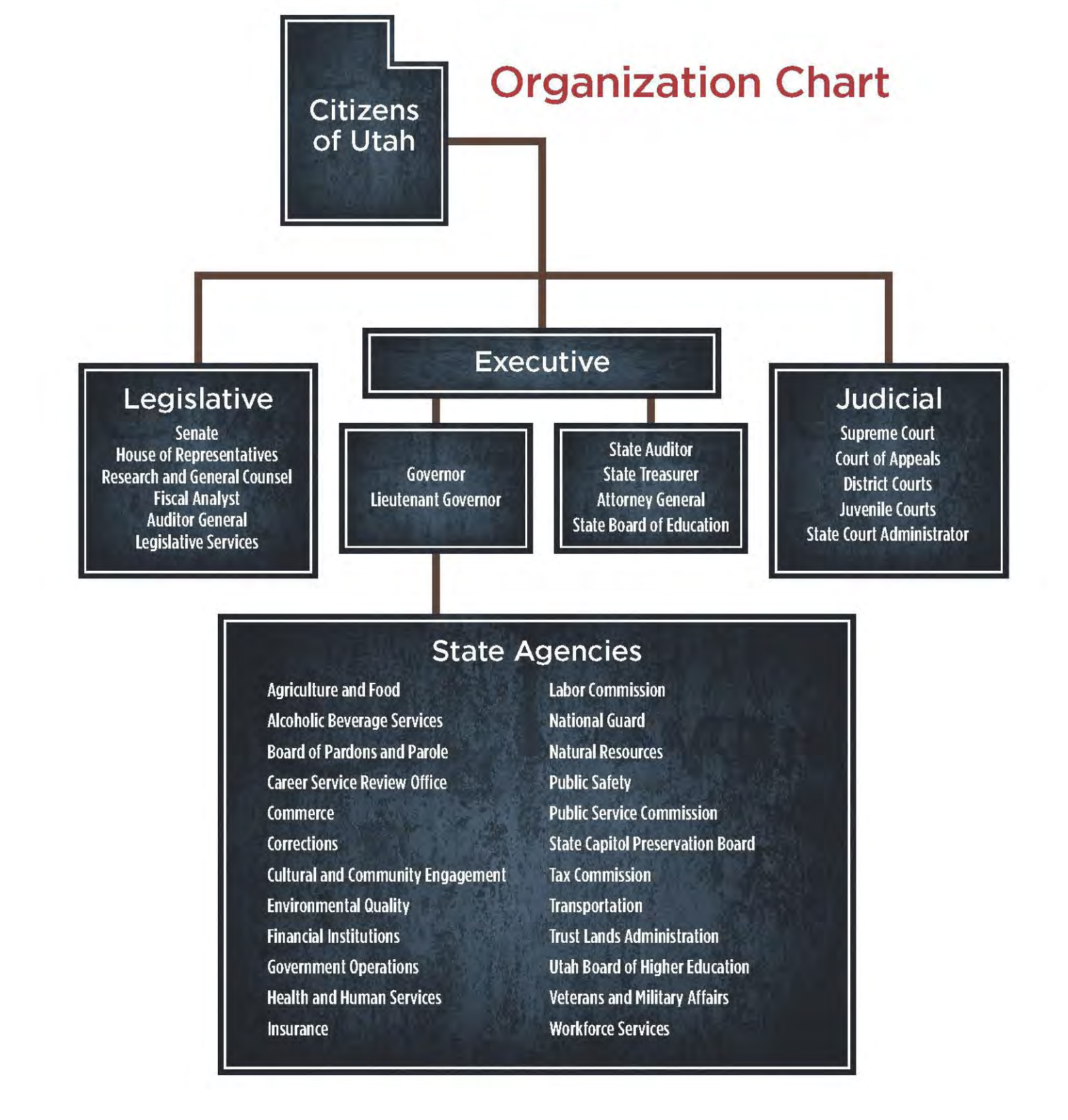
Utah State Board of Education (USBE)
The USBE is responsible for setting education policy and standards for K-12 public schools in Utah. The board is made up of 15 elected members who serve four-year terms.
Utah State Charter School Board (USCSB)
The USCSB is responsible for authorizing and overseeing charter schools in Utah. The board is made up of seven members who are appointed by the governor and confirmed by the state Senate.
Utah System of Higher Education (USHE)
USHE is responsible for overseeing Utah’s public colleges and universities, including the University of Utah, Utah State University, and Weber State University, and Utah Tech University. USHE sets policy and standards for higher education in Utah, and works to ensure that all Utahns have access to affordable, high-quality education beyond high school.
Utah Colleges of Applied Technology (UCAT)
UCAT is responsible for overseeing Utah’s technical colleges and vocational training programs. UCAT provides training and certification in a variety of fields, including healthcare, construction, and technology.
Overall, the governance of education in the United States is a complex system involving multiple levels of government and a variety of stakeholders. This system is designed to ensure that all students have access to sound education.
Utah Education Network (UEN)
A collaborative network of public and higher education institutions in Utah that provides digital resources and support for teaching and learning.
Laws that Affect the Governance of Education
Federal Education Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) also know as the Buckley Amendment
FERPA protects the privacy of student records. This law provides for the right to inspect and review educational records, the right to seek to amend those records and to limit disclosure of information from the records.
Education and the 14th Amendment (Equal Protection Clause)
Under the the 14th amendment to the US constitution, if a state establishes as public school system, no child may be denied an education within that system.
Equal Protection Clause
No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.
While education may not be a “fundamental right” under the Constitution, the equal protection clause of the 14th Amendment requires that when a state establishes a public school system, no child living in that state may be denied equal access to schooling.
10th Amendment
According to the 10th Amendment, the federal government can only exercise powers granted by the Constitution, and states or individuals can exercise control over matters not delegated to the federal government such as education.
Governance
The system of policies, regulations, and decision-making structures that guide the operation of schools and other educational institutions.
Policies
Rules or guidelines that are established to direct actions or decisions.
Regulations
A set of official rules or laws that are established by an authority to ensure compliance.
Federal Government
The national government of the United States, which is responsible for developing policies related to education, providing funding to schools and districts, and monitoring compliance with federal laws.
State Government
The government of an individual state that provides most of the funding for public education, and establishes standards for student achievement, teacher certification, and school accountability.
Local Government
The government of a county or city that is responsible for managing individual schools and providing education services to students.
Department of Education
The U.S. Department of Education is responsible for developing policies related to education, providing funding to schools and districts, and monitoring compliance with federal laws.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
A federal law that guarantees certain rights to children with disabilities, including the right to a free and appropriate public education.
State Departments of Education
State-level agencies responsible for implementing and enforcing education policies and regulations.
School Districts
Local organizations responsible for managing individual schools and providing education services to students.
School Board
Elected bodies responsible for setting policies and overseeing the operation of schools within a district.
Educational Reforms
Educational reforms refer to the changes made to the educational system in order to improve it. These reforms can include changes in curriculum, teaching methods, assessment methods, teacher training, and funding. The aim of educational reforms is to improve the quality of education and ensure that all students have access to a high-quality education that prepares them for success in the future.
Some of the more common educational reforms in the past 35 years include:
A Nation at Risk 1983 (Regan Administration)
No Child Left Behind 2002-2015 (Bush Administration)
Common Core State Standards 2010-present (Board of Governors)
Every Student Succeeds Act 2015 (Obama Administration)
Vocabulary
Federal Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
School Governance
Policies
U.S. Department of Education
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
No Child Left Behind
State Government
Utah State Board of Education (USBE)
Teacher Certification
Local Education Agency (LEA)
School Board
Property Taxes
Principal
Utah Education Network (UEN)
Utah Colleges of Applied Technology (UCAT)
Utah State Charter School Board (USCSB)
Utah System of Higher Education (USHE)
ESSA
Common Core
A Nation at Risk
