Respiratory Volumes and Capacities
Objective 6
State the four respiratory volumes and four respiratory capacities. Identify each of these on a spirogram.
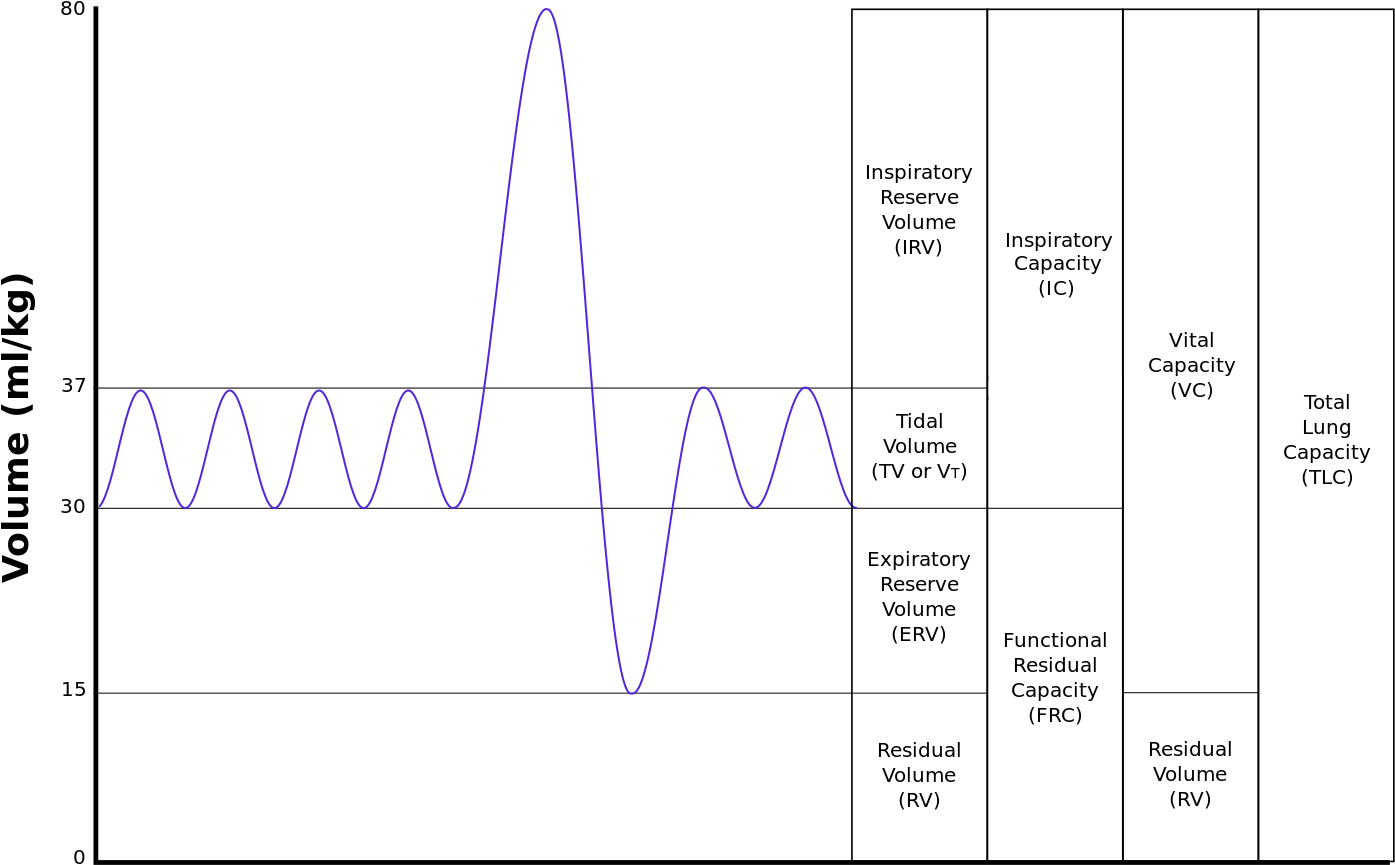
Pulmonary function can be tested using a spirometer, which measures the volume of air exchanged during breathing and the respiratory rate. The record of this measurement is called a spirogram. Four respiratory volumes and four respiratory capacities are measured.
The four volumes are:
Tidal Volume (VT): Volume of air inspired or expired during normal quiet breathing.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume: All of the air that you can breathe in from the top of tidal volume (during a very deep inhalation).
Expiratory Reserve Volume: All of the air that you can breathe out from the bottom of tidal volume (during a forced exhalation).
Residual Volume: Air still present in lung tissue after maximal exhalation. It is what keeps the lungs open even after we have breathed out all that we can.
The four respiratory capacities are combinations of specific lung volumes:
Inspiratory capacity: The sum of tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume.
Functional residual capacity: The sum of residual volume and expiratory reserve volume.
Vital capacity: The sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and expiratory reserve volume.
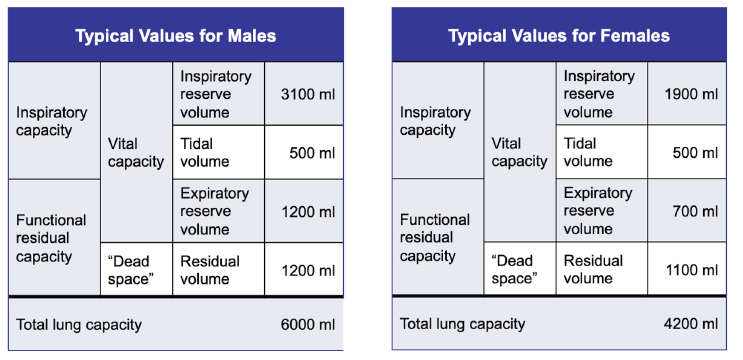
Total lung capacity: Sum of vital capacity and residual volume. Total lung capacity is around 6000 mL for males and 4200 mL for females. See the tables here for representation of the estimated volumes.
Media Attributions
- U17-037 Lung Volumes © Kapwatt is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- U17-038 Respiratory Volume Tables © Burr, Justin is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license

