Lateral Medullary Syndrome (Wallenberg Syndrome)
Brooke Hildt and Jim Hutchins
Overview
https://radiopaedia.org/articles/lateral-medullary-syndrome?lang=us
1/5 strokes in posterior circulation
lateral medullary syndrome is the most common of the posterior circulation strokes
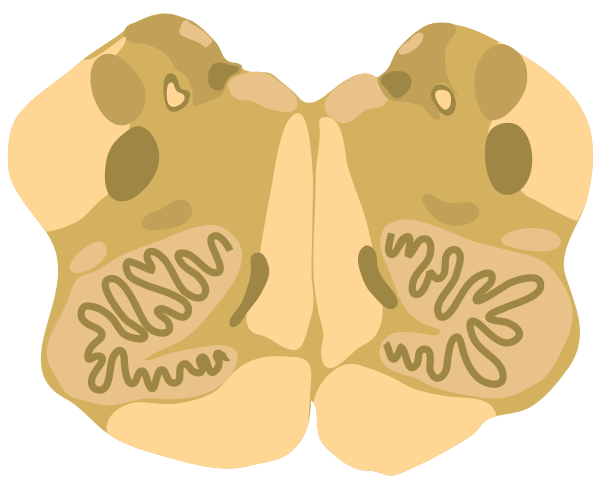
Structures affected
- inferior cerebellar peduncle
- dorsolateral medulla
- descending spinal tract
- nucleus of the V nerve
- vagus nerve and nucleus
- glossopharyngeal nerve and nucleus
- descending sympathetic fibers
Signs and Symptoms
- vestibulocerebellar symptoms
- ipsilateral hemiataxia
- vertigo
- falling toward side of lesion
- multidirectional nystagmus (inferior cerebellar peduncle and vestibular nucleus)
- autonomics
- ipsilateral Horner syndrome
- hiccups
- sensory
- loss of p&t over ipsilateral face & contralateral body
- bulbar
- hoarseness
- dysphonia
- dysphagia
- dysarthria
- decreased gag reflex (nucleus ambiguus)
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Wallenberg Syndrome includes a clinical examination, patient history, MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging, angiogram, and/or an EKG.
Treatment
Treatment will vary based on the cause of Wallenberg Syndrome. Possible treatment interventions include IV administration of thrombolytic drugs, surgery to remove clots/ repair a damaged artery, and possible long-term rehabilitative therapies.
Risk Factors
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Neck injuries
Case Study
Media Attributions
- Medulla_-_Middle_level_cross_section.svg © Kevin Dufendach is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license

