1
LENNOX-GASTAUT SYNDROME
Introduction
Lennox-Gastaut (LGS) is an uncommon pediatric epilepsy syndrome that makes up around 10% of childhood epilepsy. Lennox-Gastaut is characterized by the onset of multiple different seizure types, severe cognitive delay, and a distinct EEG pattern.
History
Lennox-Gastaut is named after the two physicians who first documented the disease. In the 1950’s, Dr. William Lennox described a particular EEG finding that would match an epilepsy syndrome that Dr. Henri Gastaut was studying in the mid 1960’s. Dr. Henri Gastaut described a childhood epilepsy with frequent tonic and absence seizures. Later it was found that both Dr. Lennox and Dr. Gastaut were studying the same epilepsy syndrome and thus it was coined Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Symptoms
Lennox-Gastaut is frequently associated with intractable epilepsy, severe cognitive impairment, and a characteristic EEG pattern.
Epilepsy
Patients with Lennox-Gastaut tend to present with multiple seizure types.
- Tonic
- Tonic-Clonic
- Atonic (Drop attacks)
- Myoclonic
- Atypical Absence (With characteristic EEG pattern)
Seizures in patients with Lennox-Gastaut are frequent in nature and tend to cluster which makes them high risk for progressing into Non-convulsive status epilepticus (NCSE).
The average age of seizure onset in patients with LGS is between 3-5 years of age. Almost all patients with an LGS diagnosis have an onset of seizures before 8 years of old.
Cognitive Impairment
Cognitive impairment before seizure onset is seen in roughly half of patients. Depending on the severity of the disease there may be a delayed onset of cognitive delay until after the patient has had their first seizure.
Characteristic EEG pattern
EEG in patients with LGS can be complex and difficult to read. Due to the multitude of seizure types, there are different ways that LGS may present. However, in LGS there is one very characteristic EEG pattern known as atypical absence which helps to set it apart from others.
Atypical absence seizures are defined as slow (1.5-2.5 Hz) irregular polyspike discharges. It is important to note that atypical absence seizures differ from typical absence seizures in that they are slower (Typical absence seizures tend to be in the 3-5 Hz range) and are often asymmetric (Typical absence seizures are almost always generalized). Atypical absence seizures are NOT triggered by hyperventilation.
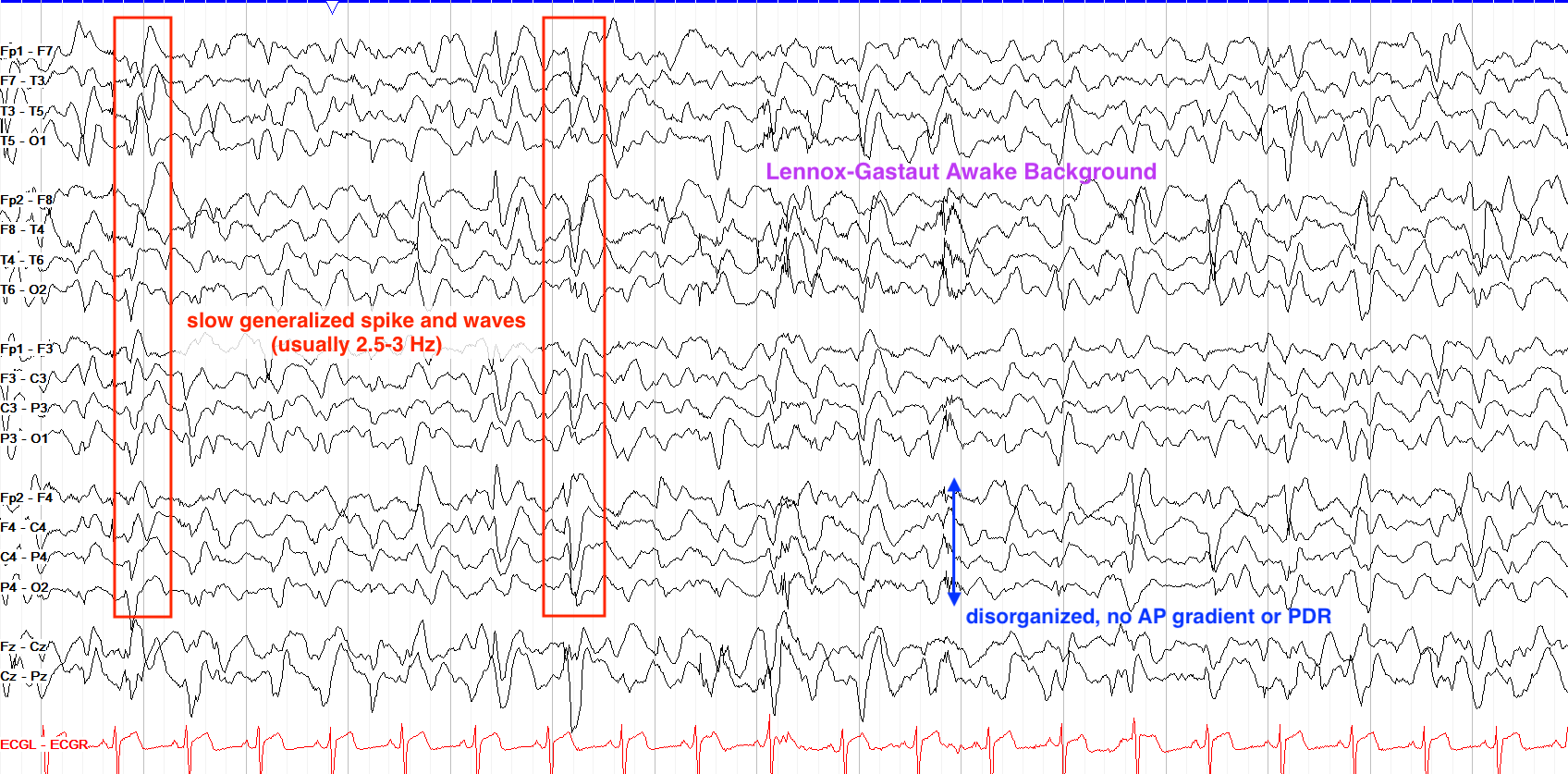
From “The Pediatric EEG”, by David Valentine M.D., 2020, (https://www.learningeeg.com/pediatric). Copyright 2020 by David Valentine
Figure 2.2 showing Lennox-Gastaut awake background with 2-2.5 Hz generalized spike and wave.
Other patterns that can be seen in Ictal EEG of an LGS patient include:
- Rhythmic, high amplitude discharges in the high alpha-beta ranges seen in tonic seizures.
- Arrhythmic bursts of polyspike and wave discharges seen in myoclonic seizures.
Classifications of disease
LGS diagnoses typically fall into the following two categories: Secondary & Idiopathic
Secondary LGS:
This accounts for about 75% of all cases and describes a known primary cause. Any damage to the brain before or during birth can be considered a primary cause to LGS. These include:
- Infection
- Frontal lobe injury
- Tuberous Sclerosis
- Perinatal asphyxia
- Perinatal stroke
- Abnormal development
Idiopathic LGS
These account for the other 25% of LGS cases and have no known cause.
Linkage between Lennox-Gastaut & West Syndrome
An LGS diagnosis has been to known to frequently follow a myriad of other childhood epilepsy diagnoses. None are more common than the diagnosis of West Syndrome, as many LGS cases follow a diagnosis of West Syndrome despite no known cause for the linkage of the two.
Treatments & Prognosis
Long-term prognosis is generally unfavorable for patients with LGS. While mortality secondary to LGS is low, severe cognitive impairment and treatment resistant epilepsy still persists in the majority of patients. Patients with a history of West Syndrome also tend to have worse outcomes than those with idiopathic LGS.
Treatment options in LGS vary due to the multitude of seizure types. Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) tend to be the mainline treatment for LGS but rarely does a single AED give complete relief of seizures. Valproic Acid (Depakote) and Lamotrigine (Lamictal) are the most commonly used AEDs in LGS. Other forms of treatment include the Ketogenic Diet, VNS, and surgical intervention. LGS patients are good candidates for corpus callosotomy to help reduce the frequency of seizures, though it is rare for surgical intervention to be completely curative.
Interactive Case Study
Key Takeaways
- 1.5-2.5 Hz Absence seizures are a common EEG finding in patients with LGS.
- LGS is likely to be secondary to some form of neurological damage before or during birth.
- There is a common progression of West Syndrome to Lennox-Gastaut.
- Valproic acid is the mainline treatment for LGS, followed by a variety of other AEDs as needed.
Difficult to treat
Continuous contraction of 1 or more muscles
Tonic: A stiffening of the muscles
Clonic: A characteristic twitching or "Jerking" of the muscle
Tonic-Clonic: Alternating periods of both stiffening of the muscle succeeded by rhythmic twitching.
Sudden loss of muscle tone
Short duration jerking
Arising spontaneously or from an obscure or unknown cause
Vagus Nerve Stimulation
